- #1
Temp89
- 7
- 0
Hello, I'm building a DC generator for fun (of the cardboard and lego variety). It is based on this model:
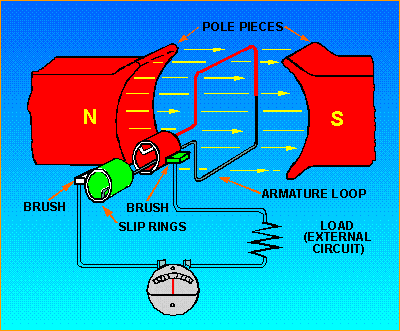
How would you calculate the power output from that, assuming we know the strength of the magnets and the frequency of rotation?
Are there any easy ways to increase output/efficiency without significantly altering the model or adding too much weight to the armature?
I'm embarrased to say I don't know the difference between an AC and DC generator. Which one is better?
I also heard that something along the lines of electrical friction slows down the turns of the armature. Will this make it too inefficient to power anything like one of those mini-bulbs?
Thanks.
How would you calculate the power output from that, assuming we know the strength of the magnets and the frequency of rotation?
Are there any easy ways to increase output/efficiency without significantly altering the model or adding too much weight to the armature?
I'm embarrased to say I don't know the difference between an AC and DC generator. Which one is better?
I also heard that something along the lines of electrical friction slows down the turns of the armature. Will this make it too inefficient to power anything like one of those mini-bulbs?
Thanks.