- #1
frascati
- 25
- 0
EE is not my forte. Although this little circuit is so simple that I could get myself 90 percent there, it performs such an important function that I would like to get it more like 99 percent correct.
I want to add the circuit to this board
http://www.ebay.com/itm/Finished-board-New-TPA3123-2-1-digital-power-amplifier-board-subwoofer-output-/251210310744?
I already fried one board. Another is on order and I'm "bench testing" it with a number of SMPS ranging from 15vdc@3.0amps to 20vdc@5.0amps.
Below is the source of the protection circuit I want to add.
Is it possible to calculate the correct value/capacity for diode/resistor/pmos fet from the description I've given of the power sources and amplifier used?
I want to add the circuit to this board
http://www.ebay.com/itm/Finished-board-New-TPA3123-2-1-digital-power-amplifier-board-subwoofer-output-/251210310744?
I already fried one board. Another is on order and I'm "bench testing" it with a number of SMPS ranging from 15vdc@3.0amps to 20vdc@5.0amps.
Below is the source of the protection circuit I want to add.
Is it possible to calculate the correct value/capacity for diode/resistor/pmos fet from the description I've given of the power sources and amplifier used?
P-Channel FET
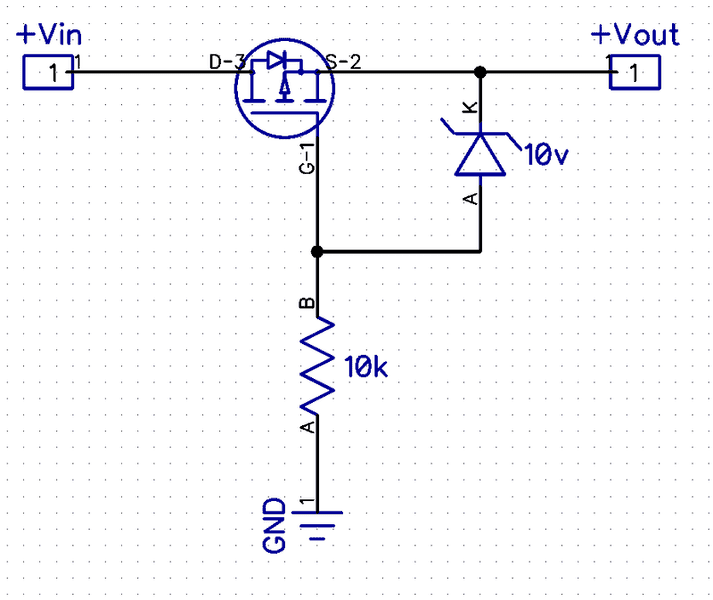
For the ultimate in low voltage drop and high current capability, replacing the PNP transistor with a P-channel MOSFET as shown in this circuit, can’t be beat. Please note that the FET is actually installed in the reverse orientation as it would normally – the drain and source are reversed. This orientation is necessary so that the slight leakage current through the FET’s intrinsic body diode will bias the FET on when the polarity is correct and block current when reversed, thus shutting off the FET. Here is a real nice video tutorial of how the magic works.
If the supply voltage is less than the FETs maximum gate to source voltage (Vgs), you only need the FET, without the diode or resistor. Just connect the gate directly to ground. I have found that most smaller FETs maximum Vgs is 12 volts or less, which can be a problem for 12 volt (or higher) supplies. If after checking your FET’s spec sheet, you find that Vcc could exceed the maximum Vgs, then you must drop the voltage between the gate and the source.
The circuit shown does exactly that by a very clever means. By inserting a zener diode with a voltage less than the maximum Vgs, it limits the voltage to a safe level between the gate and the source. You will need to calculate the resistor value so that it will provide enough current to properly bias the zener diode chosen. The zener diode’s spec sheet will provide the minimum current required to achieve the zener breakdown voltage, and you can then calculate your resistor value from that.
