- #1
- 565
- 449
- Homework Statement
- How can the circuit shown below be used to measure the qubits b0 and b1 for equality without learning anything else about the state of b0 and b1? (Hint: you are free to choose any initial state on the register consisting of qubits a0 and a1.)
- Relevant Equations
- Cnot = |0⟩⟨0|⊗I + |1⟩⟨1| ⊗X
This is the given circuit:
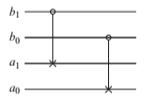
I think to add another Cnot on the right with a1 as control and a0 as target, to set initial states of a0 an a1 both |0⟩, and to measure the a0. If a0=|0⟩ then b0=b1, and vice versa.
Is it correct?
I think to add another Cnot on the right with a1 as control and a0 as target, to set initial states of a0 an a1 both |0⟩, and to measure the a0. If a0=|0⟩ then b0=b1, and vice versa.
Is it correct?