- #1
jeremyfiennes
- 323
- 17
- TL;DR Summary
- The two seem contractory. How are they reconciled?
The GR predictions for the universe's size are those of fig.a. Whereas the Hubble expansion is exponential, fig.b. How are the two reconciled?
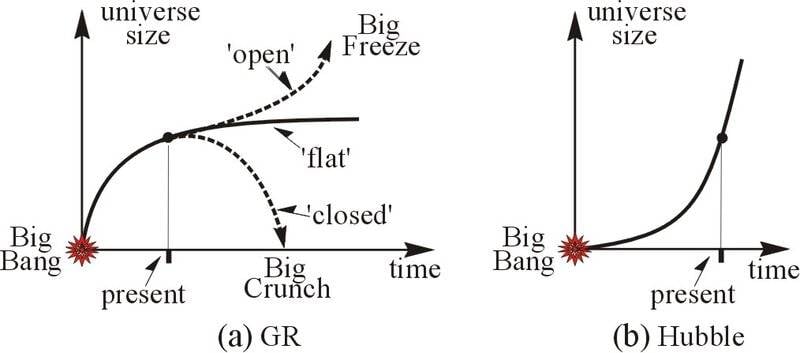
Where are you getting that figure from?jeremyfiennes said:The GR predictions for the universe's size are those of fig.a.
What "Hubble expansion" are you talking about? Where are you getting that figure from?jeremyfiennes said:the Hubble expansion is exponential
Need I point out that this means they are not valid references?jeremyfiennes said:I don't know. My memory doesn't go back that far.