- #1
Avi1995
- 21
- 0
Plz help me out with this difficulty. Here is a figure showing two conducting spheres(haven't drawn all EF lines):-
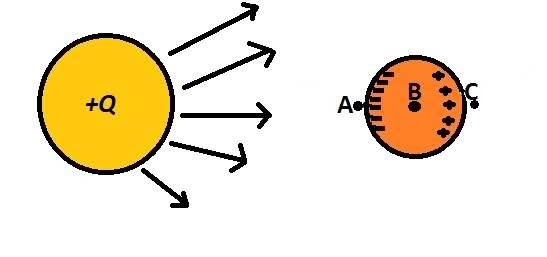
Here is the problem, Suppose one of the spheres is charged with a charge +Q, other is neutral
, so charges will get induced as shown in figure. The left portion of orange sphere(neutral one)
is at lower potential than the right portion because it has -ve charge and other is +ve.
Since E=0 inside a conductor, we have:-
dV=-E.dr
so if we move from the point A(on left surface) to B, since E=0 we have,
dV=0
so VA =VB
Now if we move from the point C(on right surface) to B, since E=0 we have,
dV=0
so VB =VC
but Va<Vc??
What is wrong in this reasoning?
dV=-E.dr
Here is the problem, Suppose one of the spheres is charged with a charge +Q, other is neutral
, so charges will get induced as shown in figure. The left portion of orange sphere(neutral one)
is at lower potential than the right portion because it has -ve charge and other is +ve.
Since E=0 inside a conductor, we have:-
dV=-E.dr
so if we move from the point A(on left surface) to B, since E=0 we have,
dV=0
so VA =VB
Now if we move from the point C(on right surface) to B, since E=0 we have,
dV=0
so VB =VC
but Va<Vc??
What is wrong in this reasoning?
Homework Equations
dV=-E.dr