- #1
pyroknife
- 613
- 4
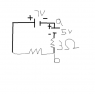
Homework Statement
I attached the pic of the problem. Note: I left half the diagram off because this part of the question only concerns this part. It wants me to find the potential difference between point a and point b. The answer is supposed to be 1V, but I don't get why. The current was for the 3 ohm resistor was given to be 2A (you won't get this answer if you try to solve for it because I left out half the diagram). When you move down the wire you gain 5V then drop (3)(2) which gives -1V. Am I misunderstandingthis question?