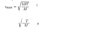- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Finding the Root Mean Square Speed of Methane at 50°C
In summary, the conversation was about finding the root mean square speed of Methane at a temperature of 50 degrees Celsius. The person was unsure of which formula to use and there was confusion over the units and meaning of the formulas. The correct formula was determined to be the first one, with the gas constant and molar mass taken into account. The conversation ended with confirmation of the correct molar mass and appreciation for the help.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
cupid.callin
- 1,132
- 1
1 i guess
what is the 2nd one for
what is the 2nd one for
- #3
omni
- 192
- 1
well 2 is T= temperature and M=Molar mass.
i also think is 1 but i wasen't sure.
by the way what R mean in the 1 formula ?
thank you.
i also think is 1 but i wasen't sure.
by the way what R mean in the 1 formula ?
thank you.
- #4
cupid.callin
- 1,132
- 1
its universal Gas constant
- #5
eczeno
- 242
- 0
equation 1 is correct if T = temperature (in kelvins), R = the gas constant, and M= the molar mass.
I cannot see how formula 2 is meaningful. it certainly does not have the units of velocity.
I cannot see how formula 2 is meaningful. it certainly does not have the units of velocity.
- #6
omni
- 192
- 1
ok i think i will try to keep on from here thanks to both of you. :)
- #7
- #8
eczeno
- 242
- 0
the physics looks good. i cannot verify that you have the correct molar mass, but i assume you looked it up in a reputable source. :)
cheers
cheers
- #9
omni
- 192
- 1
well the molar mass CH4 16.0426.
- #10
omni
- 192
- 1
and sure thanks for helping :)
- #11
eczeno
- 242
- 0
cheers
FAQ: Finding the Root Mean Square Speed of Methane at 50°C
What is root mean square speed?
Root mean square speed is a measure of the average speed of particles in a gas or liquid. It takes into account the velocities of all the particles in a system and gives a single value that represents the average speed of the particles.
How is root mean square speed calculated?
The root mean square speed is calculated using the formula v(rms) = √(3RT/M), where v(rms) is the root mean square speed, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and M is the molar mass of the gas or liquid.
What is the significance of root mean square speed?
Root mean square speed is significant because it helps us understand the behavior and properties of gases and liquids. It is directly related to temperature and molar mass, and can be used to calculate other important quantities such as kinetic energy and pressure.
How does root mean square speed differ from average speed?
Root mean square speed differs from average speed in that it takes into account the velocities of all the particles in a system, while average speed only considers the average of all the individual speeds. This means that root mean square speed is a more accurate representation of the overall speed of the particles.
What factors affect root mean square speed?
The root mean square speed is affected by temperature, molar mass, and the nature of the particles (such as their size, shape, and intermolecular forces). As temperature increases, so does the root mean square speed, while an increase in molar mass leads to a decrease in root mean square speed. Changes in the nature of the particles can also impact the root mean square speed.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 965
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 472
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 18K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 461
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 2K
Share: