- #1
Lost4468
- 3
- 0
I'm not sure about the force 3 wires have, here's the question.
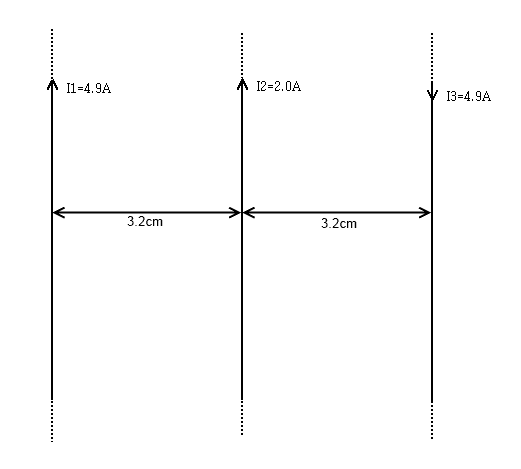
The question is:
"Calculate the force per unit length experienced by the middle wire in the arrangement shown."
The thing is I've an overall force of 0 because I1 and I3 are in different directions each producing a force of 0.15Nm^-1. Surely that's wrong? I think the middle wire somehow has an effect but I don't know how.
The question is:
"Calculate the force per unit length experienced by the middle wire in the arrangement shown."
The thing is I've an overall force of 0 because I1 and I3 are in different directions each producing a force of 0.15Nm^-1. Surely that's wrong? I think the middle wire somehow has an effect but I don't know how.