- #1
Curieuse
- 51
- 1
Homework Statement
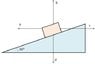
The problem wants me to order the choice for the directions of a force F of a constant magnitude F(a,b,c,d are unit vectors along which F has to be oriented) exerted on the block placed on an incline at 30° to the horizontal based on the normal force Fn that the incline would exert on the block in each case. attached: w.jpg is the pic with the question
2. The attempt at a solution
I've attempted this from two coordinate frames! One inclined with the plane and the other horizontally aligned with the base of the incline! And I get the solutions as attached! I want to know why the question marked approach gives haywire answers! The other approach is for reference!
The first is the legit answer and the next one is easier because of the chosen orientation of the frame of reference but the results are illogical. Why?
0002 is the legit answer and 0003 is the illogical one
Attachments
Last edited: