- #1
Brucezhou
- 18
- 0
The problem has been shown in the picture. Because of relativity, both the guys on the ground and on the vehicle would observe length contraction. So the destination of the guy on the vehicle---the galaxy, would be more closed to him. If the vehicle is replaced with the light, which means the distance between the photons and the galaxy would be 0 based on the formula of Lorentz's Transformation. But if this was possible, we can't measure the c=3000000000m/s, since the light can reach where we are immediately without time passes.Personal Explanation1:
To solve such problem, I think the key is that photons do not have mass. So when the they speed up to c, their mass is still 0. Based on General Theorem Of Relativity, the space will not warp and no time dilation will be observed.
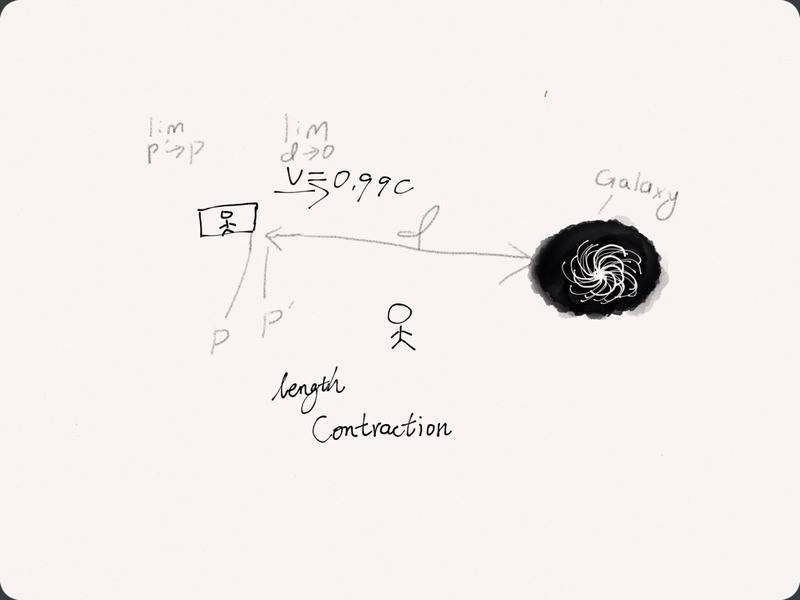
To solve such problem, I think the key is that photons do not have mass. So when the they speed up to c, their mass is still 0. Based on General Theorem Of Relativity, the space will not warp and no time dilation will be observed.