- #1
fictionistruth
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
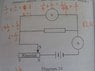
Based on the diagram attached, how do the values of current, I and voltage, V change when the sliding contact S of the rheostat is slowly moved from X to Y?
Homework Equations
Ohm's Law
R=V/I
The Attempt at a Solution
I used Ohm's Law to solve this question. My answer was: I decreases and V increases, because R is directly proportional to V and inversely proportional to I. As S is moved from X to Y, the resistance increases. I deduced that the voltage increases as resistance increases, and current decreases as resistance increases.
However my answer was wrong; the correct answer was: I decreases and V decreases. I don't understand why the voltage would decrease as resistance was increased because Ohm's Law clearly shows that R is directly proportional to V. Can anyone please explain why?