- #1
chawki
- 506
- 0
Homework Statement
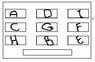
In a classroom, there are nine students, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I, sitting in three desk rows with
three students in each row. Find their places given that
- A and B are as far from each other as possible
- A, C and H are at the same distance from the wall S
- F is not in the back row
- I is in the back row
- G is in the middle of the classroom
- E and F are sitting one after the other
- E and H are at the same distance from the back wall
Homework Equations
Find their places
The Attempt at a Solution
See the pic