- #1
anj16
- 38
- 0
Hello,
In the following voltage vs time graph as we can see the voltage becomes negative often time.
My question is: if power= V*I then when voltage is negative do I have negative power?
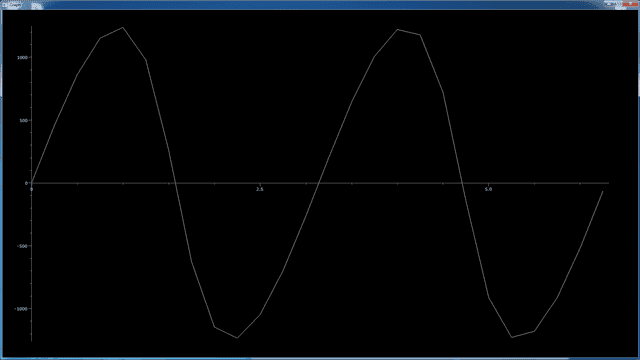
In the following voltage vs time graph as we can see the voltage becomes negative often time.
My question is: if power= V*I then when voltage is negative do I have negative power?