- #1
TS656577
- 62
- 0
[SOLVED] Friction and blocks
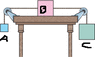
Three blocks are attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block B lies on a frictionless table; the masses are mA=6kg, mB=6kg, and mC=18kg. The accleration due to gravity is g.
F=ma
I thought that it would be wise to treat these as two separate problems. I thought I would solve one side by the following. Block B T=ma Block C F(g)-T=ma and thus mg-T=ma
I thought that to figure out the acceleration of block B (since we know C's is -9.8m/s^2) that i would use the equation a(B)=(m(C)g - (m(C)g))/m(B) But when I do that i would get 0/6. That can't be right because the block C would move because it is heavier than block A
Homework Statement
Three blocks are attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block B lies on a frictionless table; the masses are mA=6kg, mB=6kg, and mC=18kg. The accleration due to gravity is g.
Homework Equations
F=ma
The Attempt at a Solution
I thought that it would be wise to treat these as two separate problems. I thought I would solve one side by the following. Block B T=ma Block C F(g)-T=ma and thus mg-T=ma
I thought that to figure out the acceleration of block B (since we know C's is -9.8m/s^2) that i would use the equation a(B)=(m(C)g - (m(C)g))/m(B) But when I do that i would get 0/6. That can't be right because the block C would move because it is heavier than block A