- #1
- 5
- 17
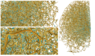
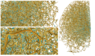
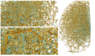
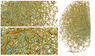
The universe was not perfectly uniform when it started, some areas had a higher density than others. During the evolution of the universe, these areas of high density contained most of the matter and started forming galaxies where there was the highest concentration of matter. This large-scale structure (‘cosmic web’) connects the observed clusters of galaxies via a series of filaments. Figure 1 is a model of what this looks like.
Figure 1: Skeleton of a cosmic web traced out by an algorithm run on a sample of observed galaxies. The far-right shows the complete web, the left images show close-up portions. Blue areas are points of higher density.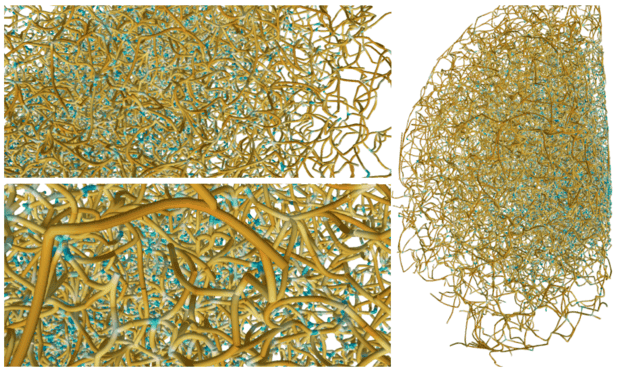
Table of Contents
1Key...
[url="https://www.physicsforums.com/insights/the-evolution-of-the-universe-cosmic-web-and-connections/"]Continue reading...
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: