Reference frame Definition and 227 Threads
-
O
B Proper time of the observer resting in CMB reference frame
Does t in a(t) in the FLRW metric correspond to the proper time of the immortal observer, who’s been resting in the CMB reference frame since its emission? -

I Energy and reference frames
I am interested in a question related to energy for different reference frames. Let's say we have two inertial reference frames A and B. The reference frame B moves relative to the reference frame A at a high speed at which relativistic effects are manifested. In reference frame B there is a...- Ivan Nikiforov
- Thread
- Energy Reference frame Relativistic effects
- Replies: 87
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I What if one is in 1905 and debating foundational fundamentals?
Einstein's theories are accepted since 100+ years. Modern science built on it somehow provides a proof of truth of his theories but what if one is living when Einstein proposed his theories and debating its merit? Einstein did two things: 1. He declared velocity of light as invariant c for all...- sandip4
- Thread
- Reference frame Velocity
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
Relative Motion: Understanding the Relationship Between Moving Objects
My attemp : ##\vec r_1## : Position of the river in reference frame. ##\vec r_2## : Position of the walker in reference frame. ##\vec r_x## : Position of the walker measured by the river. We have: $$\vec r_1 + \vec r_x = \vec r_2$$ $$\vec v = \dfrac {d \vec r}{dt} $$ $$\vec v_1 + \vec v_x =...- MatinSAR
- Thread
- Position Reference frame Relative motion
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
B Question about choice of reference frame
Hello everyone, I might be highlighting my ignorance in this post (it might be ignorance of the particulars of simultaneity) but that's a good thing because then I might be able to figure out what I don't know. If the Lorentz factor is 2 for a spaceship that is launched from Earth then...- Chenkel
- Thread
- Lorentz factor Reference frame Time dilation
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Wald synchronous reference frame proof
Hi, on Wald's book on GR there is a claim at pag. 43 about the construction of synchronous reference frame (i.e. Gaussian coordinate chart) in a finite region of any spacetime. In particular he says: $$n^b\nabla_b (n_aX^a)=n_aX^b\nabla_b \, n^a$$Then he claims from Leibnitz rule the above equals...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Coordinate chart General relativity Geodesic equation Geodesics general relativity Reference frame
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
B How to measure time in reference frame with clock?
I considered example of time dilation with light clock. I have a question about measuring time in reference frame with clock. If we know that clock move from A to B in the reference frame with clock then what time of motion is measured in this reference frame? (In non-moving reference frame...- Mike_bb
- Thread
- Reference frame Special relativity Special relativity clocks Time Time dilatation
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
B How to compare the proper times of two spatially distant mass points?
Do all synchronized clocks in a reference system always show the same time? Is this part of the definition of a frame of reference? Have the clocks always passed the same proper time from zero (see below)? Would the knowledge of the proper time of a clock between two events lead to the...- Peter Strohmayer
- Thread
- Clocks Proper time Reference frame
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
W
I Is the position vector a real vector?
Is the position vector a real vector? I have a hard time with this question because vectors are unchanged if I were to change my reference frame. Example: If I place a pencil such that it points towards the door. It doesn’t matter what I define my origin to be. The pencil’s length and direction...- WildBohr137
- Thread
- Position vector Reference frame
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

B Perception of Velocity in Special Relativity
If an object is going close to the speed of light, will outside frames of references perceive the moving object as going slow or fast?- BadgerBadger92
- Thread
- Perception Reference frame Relativity Special relativity Velocity
- Replies: 42
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Special Relativity - Which reference frame experiences which time?
This was a practice question, so it had the answer with it, which is 31 minutes. However, I'm confused as to why Lisa experiences T0. It isn't exactly an event happening in Lisa's rocket, but rather her just moving through space. From her perspective, it should look like Earth is moving at the...- AronYstad
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame Relativity Special relativity Time
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Charge density seen from a moving reference frame S' (SR + EM)
There are some question involving the statement. One of them is about the charge density in S' frame. It asks to calc it. I thought that i could calculate the electric field in the referencial frame S' and, then, use the formula $$ E = \lambda / 2 \pi \epsilon l $$ In that way, i would obtain...- LCSphysicist
- Thread
- Charge Charge density Density Em Frame Reference Reference frame Sr
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
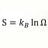
B One way speed of light in one reference frame measurement
Two clocks with photo detectors are 100 kilometers apart at A and B. On the center of AB axis two light pulses are sent to the clocks , synchronizing them. Then a light signal is sent from A to B. The two stationary observers record the time from event at A to event at B. Is there a one way...- morrobay
- Thread
- Frame Light Measurement Reference Reference frame Speed Speed of light
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
L
I Reference frame vs coordinate system
Just want to clarify some concepts. There seems to be difference between reference frame and coordinate system. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frame_of_reference#Definition . A reference frame is something has physical meaning and is related to physical laws, whereas coordinate system...- lriuui0x0
- Thread
- Coordinate Coordinate system Frame Frames of reference Reference Reference frame System
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Clarification on Rindler coordinates definition
Hi, starting from this post Basic introduction to gravitation as curved spacetime I would ask for a clarification about Rindler coordinates. From this wiki entry Rindler coordinates I understand that the following transformation (to take it simple drop ##y,z##) $$T = x\sinh{(\alpha t)} ...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Coordinate chart Coordinates Definition Minkowski diagram Reference frame Spacetime diagram
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
V
B Fluid Continuity Equation in different reference frame
If I have fluid with area 10 and velocity 10, if the velocity increases to 20 the area will become 5. But if we switch to a reference frame moving at velocity 1 opposite this motion, then it would be 10 and 11 to 5 and 21, violating the continuity equation. What is wrong?- versine
- Thread
- Continuity Continuity equation Fluid Fluid dynamics Fluid flow rate Frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Is this a reference frame problem ?
v1 - velocity of the rain with respect to the ground v2 - velocity of the man with respect to the ground v3 - velocity of the rain with respect to the man So, v1 = v3 + v2 is this right ? So, for the man moving with a velocity v2 with respect to the ground, the rain will have a horizontal...- Monsterboy
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Reference Frame, Difference in Kinetic Energy, Fuel Consumed
Say 2 cars are traveling side by side at 10 m/s in some flat, wide open space. Relative to each other they are stationary. Relative to someone on the ground they are both moving at 10 m/s. Now say you're in 1 of the cars and you see the other car accelerate, changing his velocity by 10 m/s in...- MattGeo
- Thread
- Difference Energy Frame Fuel Kinetic Kinetic energy Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

I Synchronous Reference Frame: Definition and Usage
Hi, reading the Landau book 'The Classical theory of Field - vol 2' a doubt arised to me about the definition of synchronous reference system (a.k.a. synchronous coordinate chart). Consider a generic spacetime endowed with a metric ##g_{ab}## and take the (unique) covariant derivative operator...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Frame Frobenius Killing vector Orthogonality Reference Reference frame Spacetime curvature Spacetime metric Synchronous
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Simple conceptual reference frame question
If a train is moving at some constant V with a bed sitting still on top. When the train decelerates at some rate -A then the bed will move at some acceleration A. I can't seem to get an intuition for how this comes to be. I have looked online and find no help.- Rubberduck2005
- Thread
- Conceptual Frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
I Does the CMB reference frame violate the Cosmological Principle?
Studies of the Cosmic Microwave Background shows that the Earth is moving roughly 380 km/s with respect to it towards the constellation Leo I think. Yet (I think) the Cosmological Principle and the Michelson-Morely experiments suggest there is no preferred reference frame in the universe --... -

Insights No Preferred Reference Frame: Quantum Mechanics Interpretations
Continue reading...- RUTA
- Thread
- Frame Interpretations Mechanics Quantum Quantum mechanics Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
F
Body-Fixed Reference Frame -- How is it useful?
Hello Everyone, I am trying to understand the usefulness of a body-fixed (body-centered) frame of reference ##O'x'y'z'## versus a lab frame of reference ##Oxyz##. The body-fixed frame is attached to the moving body and changes orientation exactly as the body changes orientation. From the...- fog37
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Engineering
-
F
Reference frame in collision problems
2 balls (Ball 1 and Ball 2) collide fully elastically and their relative velocity stays the same as but in sign opposite to that before the collision. Is there any sort of reference frame in which Ball 2 is always fixed (at rest) so that one can look at their relative velocity always in that... -

I Reference frame vs coordinate chart
Hello, here on PF I've seen many threads about the concepts of 'reference frame' and 'coordinate system'. In the context of SR my 'envision' about the concept of 'frame of reference' is basically the 'rods & clocks latticework' as introduced in the book Spacetime physics (Taylor, Wheeler)...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Clocks Coordinate Coordinate chart Frame Inertial reference frame Reference Reference frame Spacetime Special relativity
- Replies: 61
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
Equations of relative motion with respect to a rotating reference frame
Hi, I am just writing a post to follow up on a previous thread I made which I don't think was very clear. The question is mainly about how to use the below equations when there is also a rotation of the body around the fixed reference point. Please see the diagram here to see how the vectors...- Master1022
- Thread
- Frame Motion Reference Reference frame Relative Relative motion Rotating
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
V
I Momentary Co-Moving Reference Frame in SR
In SR, for the momentary co-moving reference frame, U (the velocity four vector) takes the form (1,0,0,0). I'm wondering whether the basis vectors associated with this velocity are zero or if the coefficients in front of the basis vectors are zero. In classical mechanics we would say that the...- Vitani1
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame Relativity Special relativity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
Question about Formulae for Motion in a Rotating Reference Frame
Hi, I am reading the following question: "Particle P moves in a circular groove with radius ## a ## which has been cut into a square plate with sides of length ## l ##. The plate rotates about its corner ## O ## with with angular velocity ## \omega \hat k ## and angular acceleration ## \dot...- Master1022
- Thread
- Formulae Frame Motion Reference Reference frame Rotating
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
B Earth Center of Mass: GR & Inertial Object Acceleration
Super-basic question that I'm embarrassed to ask. It's just what the summary says: Taking Earth's center of mass as our reference frame, how does GR account for an inertial object near the surface approaching with an acceleration of G? I assume (perhaps incorrectly) that this is an inertial...- Karl Coryat
- Thread
- Center Center of mass Frame Mass Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
I The reference frame for angular momentum components
In which coordinate system the components of angular momentum are quantized? Better to say, if we can select the coordinate system arbitrarily, how the components of angular momentum, say z-component, are always ##L_z=m\hbar##?- hokhani
- Thread
- Angular Angular momentum Components Frame Momentum Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
Rectilinear movement seen from a rotating reference frame
Let's suppose there's some platform that is rotating with angular speed omega and has a radius R. At t=0 we release some object from the border, which has an initial speed perpendicular to the radius direction with magnitude \omega R and we want to know its position at t=T with respect to the...- Livio Arshavin Leiva
- Thread
- Centrifugal force Coriolis Fictitious force Frame Inertial frame Movement Non-inertial frame Reference Reference frame Rotating
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Mechanics
-
D
B Time dilation and the reference frame of the vacuum
The point of the twin paradox in special relativity is that the traveling twin experiences a real, frame-invariant effect in which the time evolution of all moving matter is slowed down. If you read a hundred articles and textbooks on SR, you'll see a hundred variations on the message that the...- danb
- Thread
- Dilation Frame Reference Reference frame Time Time dilation Vacuum
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
A Reference frame of the vacuum -- which forum?
I have a question about interactions between matter and the vacuum, but I don't see a forum for that. Quantum field theory seems to be the most closely related subject. What would be the best forum for questions related to QFT?- danb
- Thread
- Forum Frame Reference Reference frame Vacuum
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Comoving Reference Frame in Cosmology
In cosmology, the preferred reference frame is the comoving rest frame. I am trying to understand why we are using this frame and not another one. The only reason I could come with is this. Since the expansion of the universe is homogeneous and isotropic it seems our best choice is using the... -

I Does Conservation of Momentum & Energy Hold in the C.O.M. Reference Frame?
We know classical equations fail to follow conservation of momentum and energy when we are dealing with speeds closer to the speed of light. But does it fail in the center of mass reference frame of a system?- ruivocanadense
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of momentum Energy Frame Momentum Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
T
1st Law of thermodynamics : moving reference frame
I'd like to apply the 1st law of thermodynamics in a reference frame (RF) moving with constant velocity. We have: ##\Delta{}E = E_{in} - E_{out}## I am limiting myself to rectilinear motion. Suppose we are in a RF moving with a constant velocity ##V##. Let the system consist of a mass ##m##. The...- thinkingcap81
- Thread
- Frame Law Reference Reference frame Thermodynamics
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
S
B Length Contraction in Accelerated Frame
I was wondering, would there be a length contraction (or expansion) in the z and y axis' if an object was accelerating in x axis? I know that in special relativity there is no deformation in the y and z axis' if the object is moving in the x axis. I was looking a this paper for clarification.- sqljunkey
- Thread
- Contraction Frame Length Length contraction Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Acceleration for a non-inertial reference frame
Well, first a wrote the equation for acceleration in non inertial systems. ##a_I=a_o+\dot \omega \times r+\omega \times (\omega \times r)+2(\omega \times v_{rel}) +a_{rel}##. Then, ##a_o=0## (because the system doesn't move), ##a_i=0## (because it is measured from the non inertial system)...- Like Tony Stark
- Thread
- Acceleration Frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
How Does Acceleration Transform in Special Relativity?
I'm struggling in the details of this exercise. Let ##S'## be the reference frame where the acceleration of the spaceship is constant, in which case we have ##u'(t')= a' t'## (since we assume no acceleration at the beginning). The rest frame of the rocket ##S## is connected to ##S'## via a...- Markus Kahn
- Thread
- Acceleration Proper time Reference frame Relativity Special relativity
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
M
I Inertial Mass as Speedometer: Physics & Universe
I get that the concept of relativistic mass has sort of been deprecated in physics these days and that relativistic momentum is supposed to be seen as more well useful. So let momentum equal ##\mathtt ~~ \frac {mv} {\sqrt {1 - \frac {v^2} {c^2}}} ~~## or ##~~{mv\gamma}~~##. So mass is supposed...- metiman
- Thread
- Inertial Inertial mass Mass Reference frame Relativistic mass
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Measuring position and velocity from a non inertial reference frame
I) For ##A##, the positition is ##\vec r=(0;V_0 . t;0)##. For ##B##, we have ##\vec r_A=\vec r_B + \vec r_{A/B}##, but ##\vec r_{A/B}## is equal to zero because they have the same origin, so the position measured from ##A## is equal to the position measured from ##B## II) For ##A##, velocity...- Like Tony Stark
- Thread
- Frame Inertial Inertial reference frame Measuring Position Reference Reference frame Velocity
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Entropy in a non inertial reference frame
I know that the entropy of a system is the same in different inertial frames. Is this still the case for non inertial frames? For example, is the entropy of a body as seen from a rotating reference frame the same as the entropy seen from a fixed frame?- hgandh
- Thread
- Entropy Frame Inertial Inertial reference frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

B Reference frame symmetry in Special Relativity
Hello, I have a couple of questions related to reference frames in Special Relativity. Let's consider a rocket that is inertially moving towards a star with a relative velocity 0.9c. I'd like to look at this example from both the rocket's and the star's perspectives. In the reference frame of...- x-vision
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame Reference frames Relativity Special relativity Symmetry Time dilatation
- Replies: 35
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Attribution of Reference Frame: A Dilettante's Question
I can't find an answer on my dilettante question about how we attribute reference frame to complex objects, where different parts move with different velocity or where different parts experience different influence of gravitation. For example, we can take a human's body. If we take the full...- SteveF
- Thread
- Frame General relaivity Reference Reference frame Special relativity Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
G
A Can an object be at rest in its own reference frame?
In classical physics, every object is obviously at rest with itself, and it makes perfect sense for this to be true. But would this violate the uncertainty principle for a particle? If you are the particle and you know that you're at rest with respect to yourself, you know both your location...- Grasshopper
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame Rest
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
P
Solving for c: Speed of Q2 in Q1 Reference Frame
I've tried using this equation: Where: u' = 0.86c v = 0.3c u = Is the speed of Q2 as measured by an observer in the reference frame of Q1 = 0.922c Where have I gone wrong? Have I missed a negative symbol?- Pochen Liu
- Thread
- Frame Reference Reference frame Speed
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
B Polarized Electron in a Rotating Reference Frame
I tried asking a similar question in cosmology but got no answer there so here goes... Suppose I am on a windowless spacecraft in the middle of an intergalactic void. I know that the spacecraft is spinning from measuring the centrifugal forces but have no way of observing the outside...- metastable
- Thread
- Electron Frame Reference Reference frame Rotating
- Replies: 37
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
Angular momentum of a system relative to a moving reference frame.
I don't have too much of a clue of how to begin the problem. I first wrote the angular moementum of the system of particles: →M=∑mi(→ri×→vi)M→=∑mi(r→i×v→i). Then I know that the angular momentum from of the moving reference frame would have the velocity as the sum of the velocity of the frame...- Davidllerenav
- Thread
- Angular Angular momemtum Angular momentum Frame Momentum Reference Reference frame Relative System
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Locally inertial reference frame problem
Hey PF, I am working on a problem set, and one of the problems is proving that the Christoffel symbols vanish at the origin of the coordinates ##y^{\alpha}## given by the coordinate transformation: $$y^\alpha (x) = x^\alpha - x^\alpha_{(0)} + \frac {1} {2} (x^\mu - x^\mu_{(0)} )(x^\nu -...- Pencilvester
- Thread
- Frame Inertial Inertial reference frame Reference Reference frame
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Deriving Ball Movement on Northern Hemisphere with Rotating Reference Frame
I have a ball of mass m that is situated on horizontal plane on the northern Hampshire. I am asked to show that the ball is moving, clockwise, in a manner of r = v / ( 2Ω*sin(λ) ) where v is the ball's velocity, Ω is Earth's angular velocity, and λ is the terrestrial latitude So here's what...- physicschick21
- Thread
- Advance physics Celestial mechanics Coriolis Frame Reference Reference frame Rotating
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help