Stern-gerlach Definition and 95 Threads
-

A Quantitative description of successive Stern-Gerlach measurements
I'm trying to understand how exactly we calculate the detection rate in this specific multiple Stern-Gerlach setup. As written on the image, an (unpolarized) atomic beam is sent through a three Stern-Gerlach apparatuses, and the detector supposedly clicks 25% of the time. When I try to...- Garlic
- Thread
- Measurement Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Is Calcite a parallel to the Stern-Gerlach experiment?
When light passes through Calcite it is split into two beams opposite polarizations, doubling the image, and this sounds very similar to the Stern-Gerlach experiment where atoms are split into two beams with opposite polarizations The difference is that with light the opposite polarizations are...- Frigorifico9
- Thread
- Birefringence Crystal lattice Polarization Polarized light Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 43
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Question about Stern-Gerlach experiment
I just learned about the Stern-Gerlach experiment and have some questions: 1: clearly there's no objective "up" or "down"--the directions are measured relative to the magnetic field, correct? And well always find just 2 spots of equal and opposite distance on the detector, implying the magnetic...- okaythanksbud
- Thread
- Quantum Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Who was the first to make a Stern-Gerlach experiment with two magnets?
I'm trying to fill a conceptual gap I have in the history of physics In 1922 Stern and Gerlach make their experiment, proving that electrons have intrinsic angular momentum, however it takes a while for people to understand this. At first they think this is somehow caused by quantization of...- Frigorifico9
- Thread
- Particle physics Quantu physics Quantum basics Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I When was the formula for the Stern-Gerlach experiment found?
Today we know that if you make successive Stern-Gerlach measurements the beam of atoms will split according to this formula: > cos^2 (theta/2) And this is something people back then could have figured out, they could have done many measurements, plotted the values, and realized it followed...- Frigorifico9
- Thread
- History of science Quantization Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
B Double slit experiment combined with Stern-Gerlach
A bit of background: I've read Derive the probability of spin at arbitrary angle is cos( ) | Physics Forums post in this forum and went into a "thought rabbit hole". It didn't make any sense to me and I think I made a wrong assumption somewhere along the way. Instead of typing everything out, I...- Nocturnial
- Thread
- Double slit Double slit experiment Experiment Slit Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

A Another thought experiment about spin 1/2
Let's take a beam of spin 1/2 particles prepared in the state |up> in the Z direction, let's pass it through a Stern& Gerlach apparatus in the X direction to get two beams of spin |right> and spin |left>, and then redirect these two beams directly in another inverted S&G to reunite them in one...- Christian Thom
- Thread
- Experiment Spin Spin 1/2 Stern-gerlach Thought experiment
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Stern-Gerlach experiment superposition vs mixed state
Considering SG experiment, it is usually described as if an atom in the end of its path (but before being detected on the screen) is in the superposition state, say, ##|\textsf{spin up}, \textsf{upper path}\rangle+|\textsf{spin down}, \textsf{lower path}\rangle##. Some books (Feynman lectures...- MichPod
- Thread
- Experiment Mixed Mixed state State Stern-gerlach Superposition
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
I Problem involving a sequential Stern-Gerlach experiment
An electron beam with the spin state ## |\psi\rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}|+\rangle+\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}|-\rangle##, where ##\{|+\rangle,|-\rangle\}## is the eigenstates of ##\hat S_z##, passes through a Stern-Gerlach device with the magnetic field oriented in the ##Z## axis. Afterwards, it goes...- AndersF
- Thread
- Experiment Measurement Operator Quantum mechahnics Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
C
B Is quantum superposition involved in the Stern-Gerlach experiment?
This is how I explain it, away, now: Upon entering the magnetic field the silver atom's valence electron's electric field aligns itself at right angle/s to the magnetic field, the quickest/shortest way it can, as they are wont, to do, somehow, and the rest follows, naturally. And if U are...- Curious Cat
- Thread
- Experiment Quantum Stern-gerlach Superposition
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
M
B Spin collapse in a magnetic field
Basic descriptions of spin such as the beginning of Lindley's "Where does the weirdness go" state that an electron's spin doesn't exist or is "indeterminant" until measured (e.g. passed through a Stern-Gerlach field). However, isn't the magnetic field nonzero essentially everywhere (albeit...- msumm21
- Thread
- Collapse Field Magnetic Magnetic field Measurement apparatus Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Ontology of an electron passing through a Stern-Gerlach magnet
So, as far as I think I understand, an electron that passes through a Stern-Gerlach magnet, will not have a value for its spin until that spin is measured? Does that mean the electron has no position (as given by the SGM) until measured, or that the electron does not even exist until measured?- entropy1
- Thread
- Electron Magnet Ontology Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 32
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
J
I Is Stern-Gerlach experiment a proper idealization of measurnment?
I have met statements that Stern-Gerlach experiment can be seen as idealization of quantum measurement: we start with random direction of spin (continuous), end with parallel or anti-parallel alignment (discrete). Is it a proper analogy/idealization of measurement? How to characterize the...- Jarek 31
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Why the Stern-Gerlach experiment didn't detect the L?
i recently read about the stern-gerlach experiment and found out that they did it in the first place to verify the principle of the "space quantization " introduced by Bohr , and they thought they did detect the quantization of the orbital angular momentum of ( L = 1 , m = 1,-1 ) neglecting the...- patric44
- Thread
- Dipole moment Experiment Magnetic moment Spin Stern gerlach Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
N
I Stern-Gerlach w. normal distribution if magnets were more separated?
Just wondered if the power of mags. is decreased, or they are more separated, don't you get a normal distribution ? (I'm in biology) - would you also not have predicted that w. reasonably strong magnets, they will either end one one side or the other ? Thx a lot!- ndvcxk123
- Thread
- Distribution Magnets Normal Normal distribution Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B Stern-Gerlach experiment - please confirm this surprising result
A SG device oriented along z-axis is used to prepare a stream of spin up particles from a randomised source. These are then passed through an x-axis SG device. If their spins were to be measured now they would be 50% left, 50% right. But instead, the two beams are recombined and passed through a...- Jehannum
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A Advanced models for the Stern-Gerlach experiment
A detailed discussion of measurement in the Stern-Gerlach experiment can be given in the POVM setting; see this post.- A. Neumaier
- Thread
- advanced Experiment Models Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 0
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-

I Stern-Gerlach experiment with a classical object
I want to have a make/calculate a classical analog of the SG experiment within classical physics to understand all the relevant forces at play here. Within this context i would like to stick to classical physics only (yeah, I want it to compare to QM later but that is besides the discussion) and...- Killtech
- Thread
- Classical Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

I Question on the SG (Stern-Gerlach) Spin experiment
During a SG experiment, the components N and S of the magnetic field are placed at the exact distance from the beam of particle?(or with precise approximation) What would happen if for example S is placed a little more distant from the beam of particle than N? Will we observe more deflection...- arkantos
- Thread
- Experiment Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
W
I Stern-Gerlach "interferometry"
Suppose we have a state ##|\psi\rangle \sim |\uparrow z\rangle + |\downarrow z\rangle## passing through a Stern-Gerlach magnetic field oriented in the ##\hat{z}## direction such that ##|\uparrow z\rangle##'s are pulled up and ##|\downarrow z\rangle##'s are pulled down. Then suppose we place some...- WWCY
- Thread
- Interferometry Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

A How does the thermal interpretation explain Stern-Gerlach?
I am posting this question separately from the ongoing thermal interpretation thread started by @A. Neumaier since it is a question about a specific experiment and how that interpretation explains it. The experiment is the Stern-Gerlach experiment. For concreteness, I will specify that we are...- PeterDonis
- Thread
- Explain Interpretation Stern-gerlach Thermal
- Replies: 94
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
A
A Has the 2-stage Stern-Gerlach experiment been performed?
In http://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/III_05.html#Ch5-S1, Feynman mentions that the 2-stage Stern-Gerlach experiment, which proves the electron spin states to be in a superposition, has never been actually done! I have also not seen any paper reporting such an experiment. My question is, has...- Ali Lavasani
- Thread
- Copenhagen interpretation Experiment Quantum machenics Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B Entangled electrons in the Stern-Gerlach experiment?
I have always been interested in entagled electrons. so I thought about the stern gerlack experiment and simly wondered what would happen to entagled electrons in such an experiment. (although the prefix says high school i am able to appreciate more complicated answers).- Quarky nerd
- Thread
- Electrons Entaglement Entangled Entangled particles Experiment Stern gerlach Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
W
Stern-Gerlach: Measurements of spin
Homework Statement Hi all, here's the problem I need help with: Compare the following situations : A beam of atoms has half of them preselected having spin up along z and the other half having spin down along z. This beam is sent through a Stern-Gerlach (SG) apparatus that sorts in the z...- WWCY
- Thread
- Gerlach Measurements Spin Stern Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
W
I Spin confusion: Stern-Gerlach experiment
I have some serious issues trying to understand the idea of the spin in the context of the Stern-Gerlach experiment and would appreciate some assistance! Assuming that a homogenous magnetic field ##B## in the "North-wards" ##z##-direction, assume that there is a magnetic dipole moment ##\mu##...- WWCY
- Thread
- Angular Confusion Experiment Magnetic Moment Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Spin of a charged sphere in a non-uniform magnetic field
Homework Statement Consider a solid spinning sphere of negative charge in a non-uniform magnetic field: http://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F2f8%2F2f840122-3d7f-4af3-98a7-efa9b2e7d26a%2FphpBOhfaK.png (the rotation illustrated at the top is supposed to be counter-clockwise). What...- nagyn
- Thread
- Charged Charged sphere Field Magnetic Magnetic field Motion Quantum Sphere Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
I What is the behavior of real magnets when passed through Stern-Gerlach gates?
Is there any study involving real magnets behaviour shot through Stern-Gerlach gates? I've seen something using rather large magnets[1], but still the pattern showed two bulges. I if suppose using very small magnets the split-up would be much clearer. After all these magnets are not simply...- calinvass
- Thread
- Magnets Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
I Zeeman effect after a Stern-Gerlach experiment
Let's say you take a beam of particles and pass it through a Stern Gerlach apparatus and you select one of the outgoing beams, therefore collapsing the wavefunction to certain values of orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum. If you performed the Zeeman experiment on that beam, I'm...- svletana
- Thread
- Experiment Gerlach Stern Stern-gerlach Zeeman Zeeman effect
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

How is the spin state determined after the first Stern-Gerlach experiment?
Homework Statement problem no.3 Homework Equations <ΨㅣΩㅣΨ> The Attempt at a Solution I used <ΨㅣΩㅣΨ> and but I don't find solution lΨ(t)>=? I need help...- dongwoo
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
B
Stern-Gerlach experiment Problem
Homework Statement Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution (a) : There is no interference. (b) : Interference And i don't know how to approach (c), (d)- BREAD
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
B What Happens in a Uniform Magnetic Field: The Stern-Gerlach Experiment
What effect the magnetic field would have produced had it been uniform?- nirmali
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
P
I Stern-Gerlach experiment questions
In the Stern-Gerlach experiment , they used silver ions with a an unpaired electron in the outer shell...The typical result from passing the silver ions through a Non-uniform magnetic field is to separate spatially the bean into two types of "spin"...In other words the non-uniform B filed cause...- Pet Scan
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
Stern-Gerlach experiment as a measurement
Its been a while that I'm thinking in what sense we can say the SG experiment is a measurement. What I concluded, is that there are two kinds of measurements. 1) Measurements that advocates of the ensemble interpretation (like our own @vanhees71) declare as the only one that QM has anything to...- ShayanJ
- Thread
- Experiment Measurement Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
M
What is the position dependent magnetic field for a Stern-Gerlach experiment?
Homework Statement For a Stern-Gerlach experiment, there is a apparatus designed to create a magnetic gradient. There is a dipole magnet. The radius of the convex pole is 5 cm, the radius of the concave pole is 10 cm. The convex pole as a 2 T magnetic field along its surface. (The apparatus is...- M Demov
- Thread
- Field Magnetic Magnetic field Magnetic flux Magnetism Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
A
Why no smear in Stern-Gerlach experiment?
Why do the silver atoms not exist in a superposition of states with every possible mixture of spin-up and spin-down? Thermal photons do.- Alfred Cann
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
H
Stern-Gerlach for Spin 1 Particles
https://www.sciencenews.org/node/20378 Y'all might find this interesting. John Conway and Simon Kochen's 1-0-1 theorem. I have no questions. Sorry.- Hornbein
- Thread
- Particles Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
H
Stern-Gerlach: Run Through X, Y & Z Axes?
The atoms go through a magnetic field aligned with the x axis. This separates the atoms into two groups, spin up and spin down. Run a group through such a field again and there is no change. Run a group through a field aligned with the z axis, you get two groups. Run one group through the x...- Hornbein
- Thread
- Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
How Does the Stern-Gerlach Experiment Illuminate the Electron Spin Problem?
Hello, I've been reading the Stern-Gerlach experiment, and where the concept of electron spin is introduced, am facing a problem, i.e., if you consider electron a charged rotating sphere, then the electromagnetic energy and size of the electron becomes huge! So how do you deal with this? Thanks...- Sheldon Cooper
- Thread
- Atomic physics Electromagnetic energy Electron Electron spin Quantum mechanics Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
Stern-Gerlach experiment with electric field
Hello everyone, I was re-studying some issues that I wanted to repeat in magnetism and the moment I saw the stern gerlach experiment again, I came up with a question: what would happen if we kept this experiment exactly the same, but this time we used electric field only, instead of magnetic...- superduke1200
- Thread
- Electric Electric field Experiment Field Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
S
Particle deflection in a Stern-Gerlach experiment
In the case of a beam of atoms passing between opposed magnets in a Stern Gerlach device and being deflected by the field into two different directions with 50:50 probability, could someone please clarify for me if there is a lower limit of magnetic field strength for this sorting effect to...- Sam McGowan
- Thread
- Deflection Experiment Particle Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
Finding |<+y|-θ>|^2 in terms of θ
Homework Statement What is the probability that an electron emerging from the plus channel of the first device will end up in the minus channel of the second device? Express your answer in terms of θ. (Refer to the attached image) Homework Equations This uses the outcome probability rule that...- NanoChrisK
- Thread
- Quantum Stern-gerlach Terms
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Matrix for a Stern-Gerlach apparatus
I am trying to find the matrix representing a modified Stern-Gerlach apparatus (as proposed in the Feynman lectures) with its magnetic field in the z direction and a filter that blocks spin 1/2 atoms that are in the |-z> state (thus I'll call the apparatus a SG+z apparatus). I want to use |+x>...- damosuz
- Thread
- Matrix Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Stern-Gerlach Experiment (spatial consistency of the magnetic moment)
In the Stern-Gerlach experiment, we have an inhomogeneous magnetic field aligned with the axis labeled z. The two distinct deflections are caused by the force from two distinct magnetic moments \mu = \gamma S. I understand that the spin larmor precesses around the field and that the expectation...- nmbr28albert
- Thread
- Experiment Magnetic Magnetic moment Moment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
C
Stern-gerlach with hydrogen atoms
I was looking through a physics book that has the answers in the back. this is not homework. It asks about a neutral beam of hydrogen atoms going into a strong non-constant B field. It asks how many ways will the beam split. It says the answer is 2. Why is the answer not 3. spin 1, spin 0...- cragar
- Thread
- Atoms Hydrogen Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
Stern-gerlach vs zeeman effect = paradox?
This may be a stupid question, but I am reviewing for the physics gre and can't help but see the zeeman effect and stern-gerlach experiments as contradictions. In the Zeeman effect, a neutral atom energy level will split into 3 levels (or 2 or more if take into account anomalous zeeman), but in...- Aziza
- Thread
- Paradox Physics gre Stern-gerlach Zeeman Zeeman effect
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Double Stern-Gerlach experiment
If I were to take some electrons and send them through a Stern-Gerlach experiment, then under normal conditions half of them would be deflected upward and half downward. If however, I were to make an hole in the machine where the spin up particles were detected after selection, and now instead...- hideelo
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Stern-Gerlach spin probability
So I've just been reading about the Stern-Gerlach apparatus/experiment and had some questions about the half spin probabilities... First let's say a collection of spin-half particles are sent through a S-G apparatus (which I know measures the z component of particles spin angular momentum)...- sweetdreams12
- Thread
- Probability Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
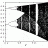
Shape of the magnet in the Stern-Gerlach experiment
Hi! In the description of the Stern-Gerlach experiment made in Sakurai's book the magnet is shaped to have a pointed edge. What is that for?- carllacan
- Thread
- Experiment Magnet Shape Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
Some questions about spin in relation to the stern-gerlach experiment
Hi, I have a few questions regarding the experimental outcome of the stern-gerlach experiment. Let's suppose the following setup: We have a magnetic field whose field-lines point towards the positive z axis and the intensity of that field becomes stronger towards the positive z axis, so there...- xortdsc
- Thread
- Experiment Relation Spin Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
I
Is the Stern-Gerlach experiment sufficient?
How experimentally it is shown that the electron's spin is hbar/2. Is the Stern-Gerlach experiment sufficient?- intervoxel
- Thread
- Experiment Stern-gerlach
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Quantum Physics