- #1
Curious314
- 31
- 0
1. A 9 volt battery is hooked up to two resistors in series. One has a resistance of 5 ohms, and the other has a resistance of 10 ohms. Several locations along the circuit are marked with letters, as shown above. If the voltage is zero at the negative terminal of the battery, the voltage at location B is
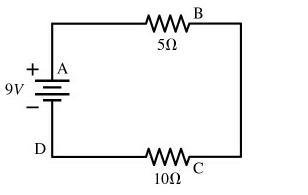
I1=I2=Itotal
I=V/R
V=I*R
I=9volts/(5+10)ohms
I=0.6A
Now we have the current in the entire circuit
with that:
Vb=0.6A*5
V=3volts
so here is my question,
at B there is 9 voltsw(wich is the total of voltage)- 3 Volts(wich is the ampunt of wolts that we took with the resistence) = 6vots?
is this the right approach or is 3 volts at location b?
Thanks!
Homework Equations
I1=I2=Itotal
I=V/R
V=I*R
The Attempt at a Solution
I=9volts/(5+10)ohms
I=0.6A
Now we have the current in the entire circuit
with that:
Vb=0.6A*5
V=3volts
so here is my question,
at B there is 9 voltsw(wich is the total of voltage)- 3 Volts(wich is the ampunt of wolts that we took with the resistence) = 6vots?
is this the right approach or is 3 volts at location b?
Thanks!