- #1
SnakeDoc
- 27
- 1
Homework Statement
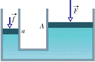
A piston of cross-sectional area a is used in a hydraulic press to exert a small force of magnitude f on the enclosed liquid. A connecting pipe leads to a larger piston of cross-sectional area A (the figure). If the piston diameters are 3.63 cm and 50.7 cm, what force magnitude on the small piston will balance a 41.8 kN force on the large piston?
Homework Equations
P=F/A
The Attempt at a Solution
So I'm pretty sure I'm doing this right especially since we did a similar one in class so I think it might just be a math error here's what I did.
For the smaller side Ps = Fs/as
For the larger side Pb = Fb/Ab
Ps = Pb
Fs/as = Fb/Ab
Solve for Fs
Fs = Fb/Ab * as
Plug in values (Fb 41.8kN = 41800N) (Ab 50.7cm =.507m) (as 3.63cm = .0363m)
Fs = (41800/.507)*.0363 = 2992.78N WileyPlus says its wrong though, so did I make a mistake?
Attachments
Last edited: