- #1
ataglance05
- 43
- 0
Airplane Free-body diagram!
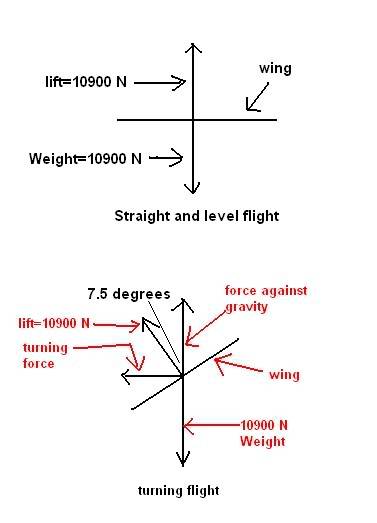
A plane with mass of 1090 kg is flying straight and level at an altitude of 1100 meters & a constant velocity of 200 kg/hr (55.55m/sec). Assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/sec^2, the force on the plane due to gravity is 10900 Newtons. Since the plane is in level flight, the net force in the y direction is 0 & the lifting force provided by the wings equals the weight of the plane. The piolot now banks the wings at a 7.5 degree angle w/ respect to the vertical in order to make a turn. Part of the lifting force of the wings is now used to make the plane turn in a circle & there's less lift to counteract the force of gravity.
How long will it take the plane to make one turn of 360 degrees at a velocity of 200 km/hr (55.55 m/sec)??
Vf=Vo+aT
S=Vo(T)+1/2(a)(T)^2
s=theta(r)
Time=Distance/radius
A free-body diagram of the situation:
NO CLUE! HELP!
All I know is that the value that the lift should be increased so that the plane doesn't decend is 10994 Newtons and that the radius of the circle that the plane will fly w/o loosing altitude w/ constant velocity of 200km/hr is 2343 m.
Homework Statement
A plane with mass of 1090 kg is flying straight and level at an altitude of 1100 meters & a constant velocity of 200 kg/hr (55.55m/sec). Assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/sec^2, the force on the plane due to gravity is 10900 Newtons. Since the plane is in level flight, the net force in the y direction is 0 & the lifting force provided by the wings equals the weight of the plane. The piolot now banks the wings at a 7.5 degree angle w/ respect to the vertical in order to make a turn. Part of the lifting force of the wings is now used to make the plane turn in a circle & there's less lift to counteract the force of gravity.
How long will it take the plane to make one turn of 360 degrees at a velocity of 200 km/hr (55.55 m/sec)??
Homework Equations
Vf=Vo+aT
S=Vo(T)+1/2(a)(T)^2
s=theta(r)
Time=Distance/radius
A free-body diagram of the situation:
The Attempt at a Solution
NO CLUE! HELP!
All I know is that the value that the lift should be increased so that the plane doesn't decend is 10994 Newtons and that the radius of the circle that the plane will fly w/o loosing altitude w/ constant velocity of 200km/hr is 2343 m.
Last edited:
