- #1
says
- 594
- 12
I'm trying to understand why peak resolution changed in my alpha spectroscopy experiment.
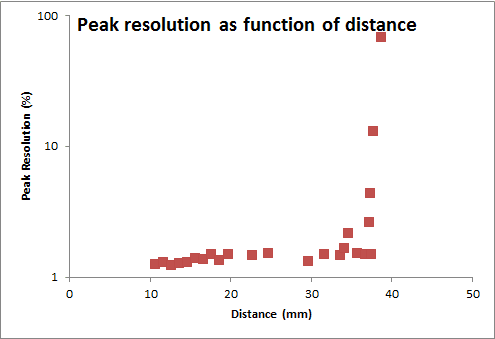
I've increased the distance between a Am-241 source and a silicon surface barrier (semiconductor) detector and taken spectra along the way, recording information about peak height and FWHM.
As the distance between the source and detector increased the FWHM got lower, but the peak resolution increased. I've calculated the peak resolution = (1/FWHM) * 100 and expressed it as a percentage.
The peak resolution has changed because the FWHM has changed. I understand that much. I don't really understand why the FWHM would decrease though. Is it purely because of the energy degradation of the alpha particles as they travel through air?
I've increased the distance between a Am-241 source and a silicon surface barrier (semiconductor) detector and taken spectra along the way, recording information about peak height and FWHM.
As the distance between the source and detector increased the FWHM got lower, but the peak resolution increased. I've calculated the peak resolution = (1/FWHM) * 100 and expressed it as a percentage.
The peak resolution has changed because the FWHM has changed. I understand that much. I don't really understand why the FWHM would decrease though. Is it purely because of the energy degradation of the alpha particles as they travel through air?
