- #1
zorro
- 1,384
- 0
An adiabatic piston of mass m...
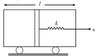
An adiabatic piston of mass m equally divides a diathermic container of volume V and length l. A light spring connects the piston to the right wall. In equilibrium pressure on each side of the piston is P. The container starts moving with acceleration a towards right. Find the stretch of the spring assuming x<< l

I just have one doubt in this question.
Is the expansion of the gas in the right part of the container adiabatic or isothermic?
Homework Statement
An adiabatic piston of mass m equally divides a diathermic container of volume V and length l. A light spring connects the piston to the right wall. In equilibrium pressure on each side of the piston is P. The container starts moving with acceleration a towards right. Find the stretch of the spring assuming x<< l
I just have one doubt in this question.
Is the expansion of the gas in the right part of the container adiabatic or isothermic?