- #1
Kumo
- 22
- 1
Hi Everyone,
A question in my latest Physics I lab wishes for a proof showing that if a laser beam is incident on a mirror that is then rotated an angle θ the beam is deflected an angle 2θ.
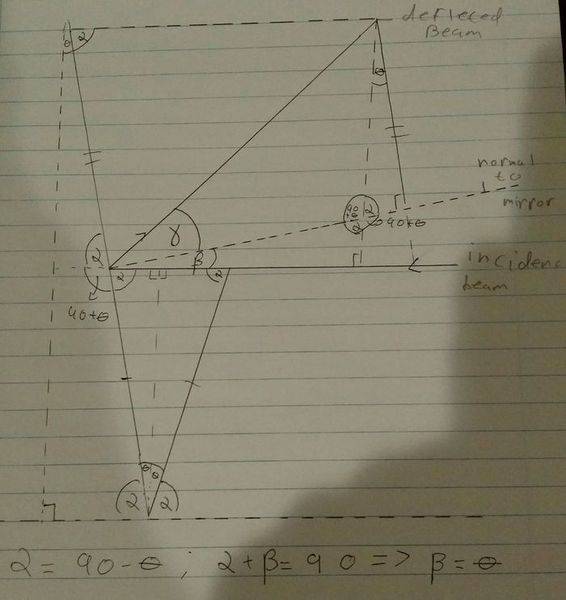
I attempted to prove this geometrically below. In the diagram the angle γ, is the angle of deflection, and β is the incident angle. I was able to show that if the mirror was rotated θ degrees to the vertical, that β = θ. However,I haven't been able to show that γ = 2θ from the below diagram, as I am unable to determine the top right/bottom left angles of the parallelogram, or any additional angles of the triangles that exist in side of it.
Any assistance or guidance would be very much appreciated.
1. Homework Statement
If a laser beam is incident on a mirror, and the mirror is rotated θ degrees, prove that the angle by which the beam is deflected is equal to 2θ.
[/B]
- Elementary geometric equations (e.g. sum of the interior angles of a triangle, properties of a parallelogram)
A question in my latest Physics I lab wishes for a proof showing that if a laser beam is incident on a mirror that is then rotated an angle θ the beam is deflected an angle 2θ.
I attempted to prove this geometrically below. In the diagram the angle γ, is the angle of deflection, and β is the incident angle. I was able to show that if the mirror was rotated θ degrees to the vertical, that β = θ. However,I haven't been able to show that γ = 2θ from the below diagram, as I am unable to determine the top right/bottom left angles of the parallelogram, or any additional angles of the triangles that exist in side of it.
Any assistance or guidance would be very much appreciated.
1. Homework Statement
If a laser beam is incident on a mirror, and the mirror is rotated θ degrees, prove that the angle by which the beam is deflected is equal to 2θ.
Homework Equations
[/B]
- Elementary geometric equations (e.g. sum of the interior angles of a triangle, properties of a parallelogram)