- #1
lirexin
- 4
- 0
Just totally confused which value to use to get the area moments of inertia with this question
The ship was initially looks like this the mass of the ship is 5000 tonnes two heavy cargocontainers each of mass 73,370 Kg each
assume that the ship has a rectangular waterline area, with length 94.85m and width 12m
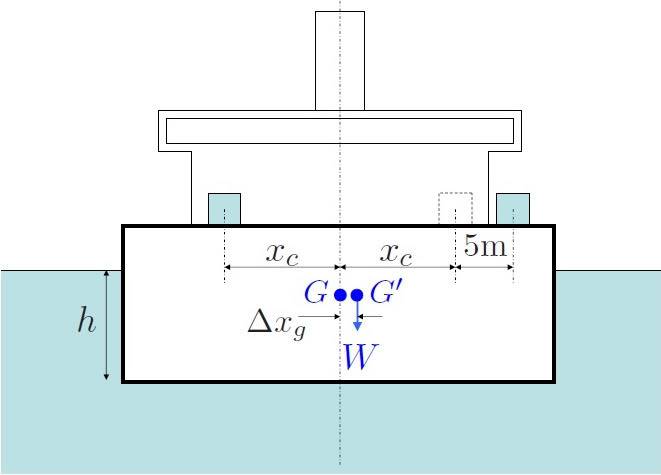
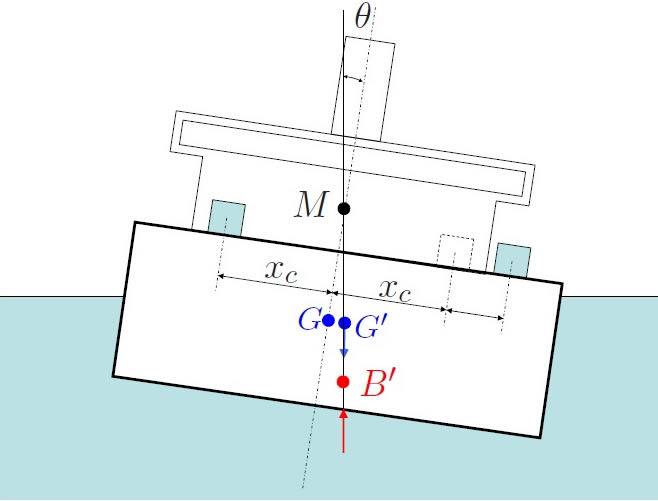
The question is asking the length of BG and hence find the length of G'B'
Ive been told that GM=47.7028(m) GG'=2.5(m) h=4.41154(m)(sink height) the angle is 3(degree)
What I've done was using the equation GM = I/V-BG then BG = I/V-GM
For the I/V part I = bh^3/12 from the textbook the problem is which value is b and which value is h?
The ship was initially looks like this the mass of the ship is 5000 tonnes two heavy cargocontainers each of mass 73,370 Kg each
assume that the ship has a rectangular waterline area, with length 94.85m and width 12m
The question is asking the length of BG and hence find the length of G'B'
Ive been told that GM=47.7028(m) GG'=2.5(m) h=4.41154(m)(sink height) the angle is 3(degree)
What I've done was using the equation GM = I/V-BG then BG = I/V-GM
For the I/V part I = bh^3/12 from the textbook the problem is which value is b and which value is h?