- #1
BWV
- 1,524
- 1,863
Volkswagen recently published this graphic supporting their decision to focus on battery-powered EVs and abandon hydrogen fuel cells
https://insideevs.com/news/406676/battery-electric-hydrogen-fuel-cell-efficiency-comparison/
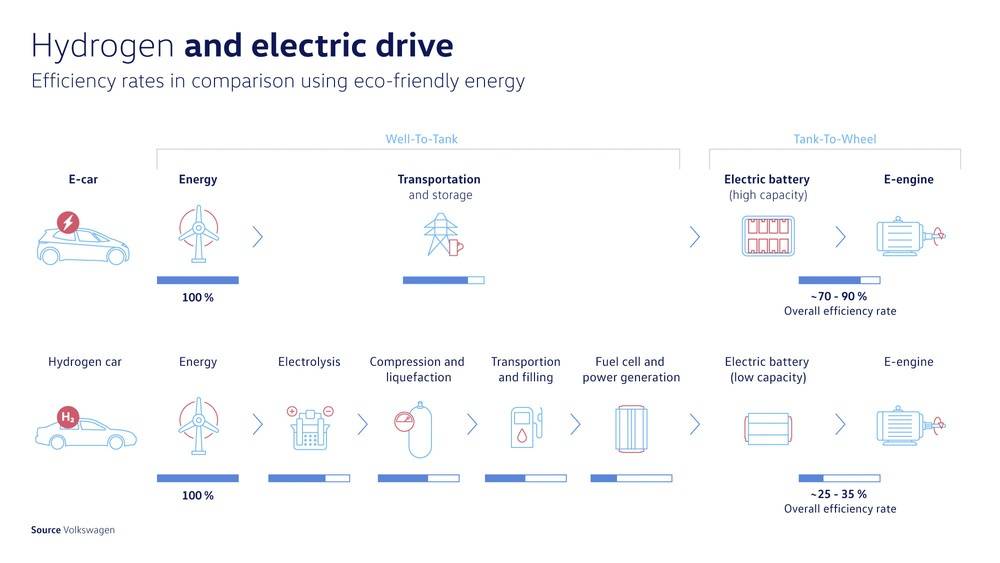
however it does not include the energy and materials required to manufacture batteries vs fuel cells. Any reason to believe that would make a difference, or is hydrogen as worthless for transportation as this implies? Note this is for green hydrogen, the electrolysis step for brown would be more efficient
https://insideevs.com/news/406676/battery-electric-hydrogen-fuel-cell-efficiency-comparison/
however it does not include the energy and materials required to manufacture batteries vs fuel cells. Any reason to believe that would make a difference, or is hydrogen as worthless for transportation as this implies? Note this is for green hydrogen, the electrolysis step for brown would be more efficient