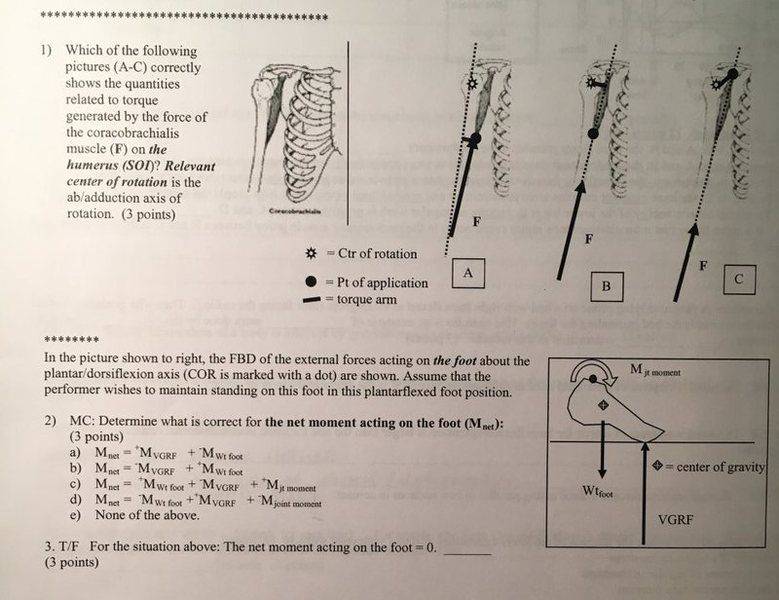
- #1
Jay B
Could anyone please help me with these problems on my biomechanics assignment? I hate asking for them to just be done for me, but I am frankly clueless given that we didn't cover torque in class yet are somehow expected to know it. Any help is appreciated, thanks!