tritonas00
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement: Calculate frequencies/gain in an AC circuit given capacitance and resistance
Relevant Equations: Looking for them :P
Hi! I have this diagram:
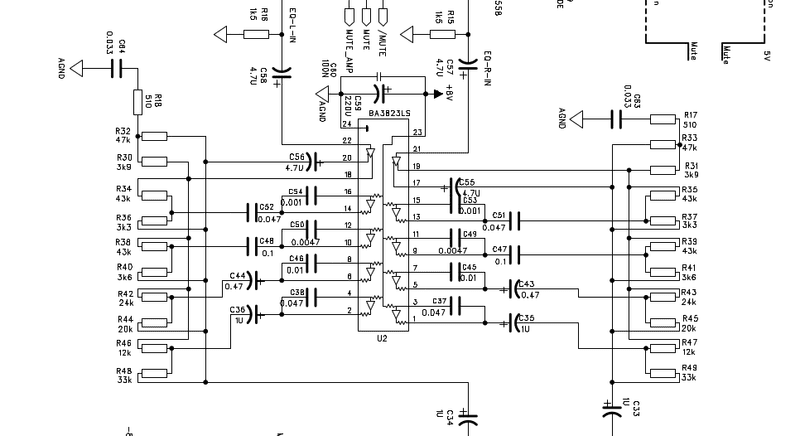
BA3823LS monolithic, five-point stereo graphic equalizer IC is used. Is there any way to calculate the frequencies (hz) that are defined and how much boost/cut gain (db) is applied in each frequency? If i'm reading this correctly the capacitors (C56, C55, ...) are used for setting the frequencies and the resistances on the side are used to cut/boost those frequencies?
I don't know anything about electronics and all the info i have is https://datasheetspdf.com/pdf-file/233435/Rohm/BA3823LS/1 where application examples of the BA3823LS are shown with the 5 center frequencies and some min/typ/max gain values.
This is not a homework, just trying to figure out what the above equalizer actually does. Thanks for your time and sorry if i'm posting this in wrong section.
Relevant Equations: Looking for them :P
Hi! I have this diagram:
BA3823LS monolithic, five-point stereo graphic equalizer IC is used. Is there any way to calculate the frequencies (hz) that are defined and how much boost/cut gain (db) is applied in each frequency? If i'm reading this correctly the capacitors (C56, C55, ...) are used for setting the frequencies and the resistances on the side are used to cut/boost those frequencies?
I don't know anything about electronics and all the info i have is https://datasheetspdf.com/pdf-file/233435/Rohm/BA3823LS/1 where application examples of the BA3823LS are shown with the 5 center frequencies and some min/typ/max gain values.
This is not a homework, just trying to figure out what the above equalizer actually does. Thanks for your time and sorry if i'm posting this in wrong section.