- #1
jaus tail
- 615
- 48
Homework Statement
v = 141.4sin(wt + 15)
i = 14.14 cos(wt - 45)
Homework Equations
Draw Phasors.
P = VI cos(theta)
Q = VI sin(theta)
S = P + jQ
theta is angle between V and I
The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
V = 141.4sin(wt + 15)
So Vrms = 141.4/1.414 sin(wt + 15)
= 100 sin (wt + 15)
I = 14.14 cos(wt - 45)
Now cos (-theta) = cos(theta)
So I = 14.14 cos (45-wt)
So I = 14.14 sin(90-45 + wt)
So I = 14.14 sin(45 + wt)
I rms = 10sin(wt + 45)
Now Vrms = 100sin(wt + 15)
I rms = 10sin(wt + 45)
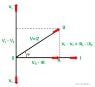
I leads V by 30 degrees.
theta = 30 degrees.
P = VI cos(theta) = 100 * 10 * cos(30) = 866W
Q = VI sin(theta) = 100 * 10 * sin(30) = 500VAR
So S = P + jQ = 866 + j500
But in answer it is given S = 866 - j500
Where does the minus sign come from?
I understand that it is leading power factor so it gives Q but mathematically sin(30) is positive value. So why should S have negative VAR?