- #1
Angello90
- 65
- 0
Hi guys,
I got this thought in my head.
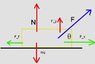
If I have a box of mass x, being pulled towards East and the angle [tex]\theta[/tex],
then force applied to the box in order to move it on the surface with friction coefficient [tex]\mu[/tex] has to be in such a way:

My question is... wouldn't N be:

Or, N would be as usual W but in opposite direction? The drawing shows all the forces on the box:
Cheers and thanks for the thought

I got this thought in my head.
If I have a box of mass x, being pulled towards East and the angle [tex]\theta[/tex],
then force applied to the box in order to move it on the surface with friction coefficient [tex]\mu[/tex] has to be in such a way:
My question is... wouldn't N be:
Or, N would be as usual W but in opposite direction? The drawing shows all the forces on the box:
Cheers and thanks for the thought