- #1
Aerstz
- 36
- 0
Homework Statement
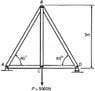
Calculate nodal forces in truss (illustrated below).
Homework Equations
Force (horizontal) = FCosTheta
The Attempt at a Solution
Force in node A (horizontal) = FCosTheta = (5000)(Cos60) = 2500 N
Force in node A (vertical) = 5000/2 = 2500 N
Force in node B (vertical = 5000 N
(no horizontal force in B)
Force in node C (vertical) = 5000 N
(no horizontal force in C)
Forces in D are the same as in A.