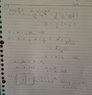- #1
MissP.25_5
- 331
- 0
I have done no. 1, but I don't how to do no. 2. Someone, please help.
Power source voltage e(t) = sqrt(2)*20sin2t [V],
current i(t) = 5sin(2t - pi/4) [A].
1. Find the values of resistance R, and inductance L.
2. Let V be the phasor of voltage v(t). Find the capacitance value of the capacitor C that maximizes the magnitude of V.
Power source voltage e(t) = sqrt(2)*20sin2t [V],
current i(t) = 5sin(2t - pi/4) [A].
1. Find the values of resistance R, and inductance L.
2. Let V be the phasor of voltage v(t). Find the capacitance value of the capacitor C that maximizes the magnitude of V.