- #1
greg997
- 109
- 2
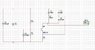
Hi can anybody explain to me how to calculate values for the resonant tank of the clapp oscillator. I know that capacitor in series with inductor sets the frequency. But I ve read that formula 1/Ceq = 1/c1+1/c2+ 1/cs, should be used to get Ceq which should be used for frequency setting. So what values of L, C1, C2, and Cs have i got to use to get like 3 MHz. I also know that Cs has to be much smaller then C1 and C2, much smaller means like 100 times?
What values of C1 and C2 to use?
I tried to make it work in multisim and included the diagram. Is it connected properly, the feedback goes from between thes tow capacitors? the Thank you
What values of C1 and C2 to use?
I tried to make it work in multisim and included the diagram. Is it connected properly, the feedback goes from between thes tow capacitors? the Thank you