- #1
furor celtica
- 69
- 0
Homework Statement
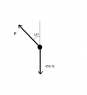
A child has weight 450 N. Whilst on a fairground ride the child is subject to a force P acting at 35° to the upward vertical, as shown in the diagram. Given that the resultant of P and the child’s weight acts horizontally,
a. Find the magnitude of the resultant
b. State the direction of the child’s acceleration
c. Find the magnitude of the child’s acceleration
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
My answers were the following
a. 315 N (to 3 s.f.)
b. The child’s acceleration is directed horizontally to the left
c. 7.00 m(s^2) (to 3 s.f.)
According to the textbook, my first two answers are correct, but the third is given as 6.86 m(s^2).
How is this possible? a = F/m = 315 / 45 = 7 m(s^2). Did I miss something?