- #1
SergeyZh
- 1
- 0
Hi there
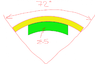
I've got a task where i need to use manual calculations with this setup (see attach.)
there is a cylinder with two internal grooves (yellow part). 5 Dogs are equally spaced (72deg.) inside that cylinder. They are being pushed by the Force against the grooves in the cylinder. What stresses i have to calculate to make sure the construction is stable with applied Force. And what equations I need to use.
I guess is only shear stress, maybe a compression stress from 45deg angle, but someone is mentioned bearing stress as well. Is there any kind of stresses i should be looking at?
Kind Regards, S.
I've got a task where i need to use manual calculations with this setup (see attach.)
there is a cylinder with two internal grooves (yellow part). 5 Dogs are equally spaced (72deg.) inside that cylinder. They are being pushed by the Force against the grooves in the cylinder. What stresses i have to calculate to make sure the construction is stable with applied Force. And what equations I need to use.
I guess is only shear stress, maybe a compression stress from 45deg angle, but someone is mentioned bearing stress as well. Is there any kind of stresses i should be looking at?
Kind Regards, S.