- #1
jjiimmyy101
- 74
- 0
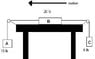
Question: The 20 lb block B rests on the surface of a table for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. Determine the speed of the 10 lb block A after it has moved downward 2 ft from the rest. Neglect the mass of the pulleys and cords.
Picture Attached
Equation: T1 + Summation of work = T2
This is what I got.
s = displacement
0 + [(Force of Friction)*(s) - (Weight of A)*(s) - (Weight of C)*(s) = 0.5*mA*v^2 + 0.5*mB*v^2 + 0.5*mC*v^2
2*2 + 10*2 + 6*2 = 0.15528*v^2 + 0.31056*v^2 + 0.09317*v^2
38 = 0.55901*v^2
v = 8.24 ft/s
Is it right?
Picture Attached
Equation: T1 + Summation of work = T2
This is what I got.
s = displacement
0 + [(Force of Friction)*(s) - (Weight of A)*(s) - (Weight of C)*(s) = 0.5*mA*v^2 + 0.5*mB*v^2 + 0.5*mC*v^2
2*2 + 10*2 + 6*2 = 0.15528*v^2 + 0.31056*v^2 + 0.09317*v^2
38 = 0.55901*v^2
v = 8.24 ft/s
Is it right?