- #1
MelanieBrett
- 7
- 0
Hi,
So for a piece of maths coursework I am thinking of trying to calculate the surface area of an atom or molecule. I do not know whether it would be viable because there isn't a clear boundary for an atom/molecule due to the electron clouds. However I wanted to know if I could do something related to this.
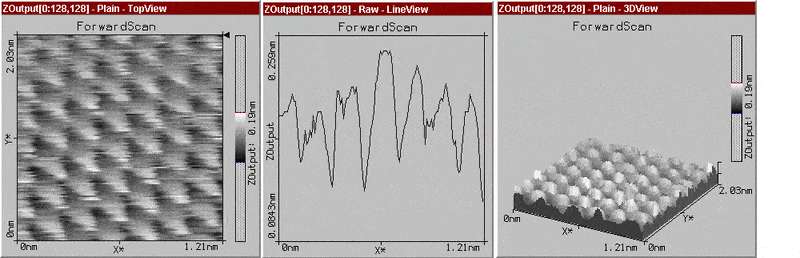
I was thinking originally of plotting a graph to the cross-section and then calculating the arc length type of thing, but it didn't really have a significance just as a cross-section. I've been thinking about taking the peaks from the cross section and assuming a regular structure and sphere type of thing and calculating it from there...
The graph I've attached is one I found on graphite, which doesn't have distinct molecules and is a hexagonal lattice
If anyone had any thoughts or ideas or better suggestions or any advice as to how I might be able to do this I would be very grateful
Thanks, B
So for a piece of maths coursework I am thinking of trying to calculate the surface area of an atom or molecule. I do not know whether it would be viable because there isn't a clear boundary for an atom/molecule due to the electron clouds. However I wanted to know if I could do something related to this.
I was thinking originally of plotting a graph to the cross-section and then calculating the arc length type of thing, but it didn't really have a significance just as a cross-section. I've been thinking about taking the peaks from the cross section and assuming a regular structure and sphere type of thing and calculating it from there...
The graph I've attached is one I found on graphite, which doesn't have distinct molecules and is a hexagonal lattice
If anyone had any thoughts or ideas or better suggestions or any advice as to how I might be able to do this I would be very grateful
Thanks, B