Ced
- 4
- 0
- Homework Statement
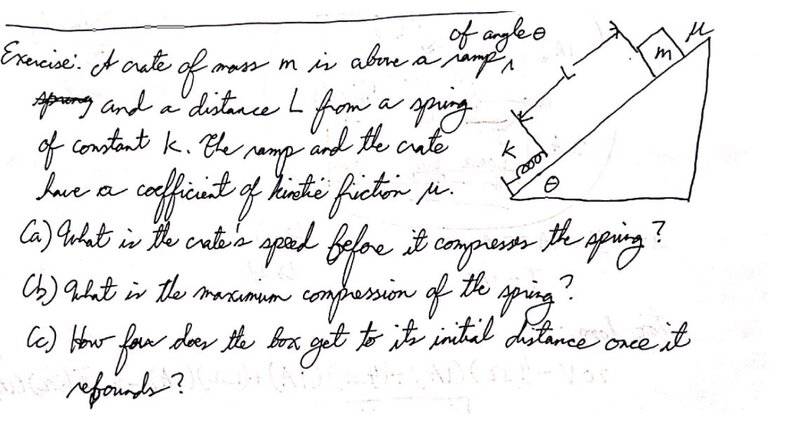
- A crate of mass(m) is above a ramp of angle theta and a distance(L) from a spring of constant k. The ramp and the crate have a coefficient of kinetic friction(μ)
a.) What is the crate's speed before it compresses the spring
b.) What is the maximum compression of the spring
c.) How far does the box get to its initial distance once it rebounds.
- Relevant Equations
- I think the relevant equations are
1. Ki + Ui + Wext = Kf + Uf
2. Elastic energy U=\frac{1}{2} k \Delta x^{2}
Here is an image for better illustration,
I only managed to solve for (a) but I'm not sure if I did it right. As for (b) and (c), I have no idea how to do it.
My answer for (a):
=> Ki + Ui + Wext = Kf + Uf
=> 0+mgh1-LμmgCosΘ = 1/2mv^2 + mgh2
=>1/2v^2 = gh1- gh2 - LμgCosΘ
=> V = √2g(h1 - h2 - LμCosΘ)
I only managed to solve for (a) but I'm not sure if I did it right. As for (b) and (c), I have no idea how to do it.
My answer for (a):
=> Ki + Ui + Wext = Kf + Uf
=> 0+mgh1-LμmgCosΘ = 1/2mv^2 + mgh2
=>1/2v^2 = gh1- gh2 - LμgCosΘ
=> V = √2g(h1 - h2 - LμCosΘ)