- #1
britt
- 32
- 0
1. The problem
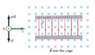
A velocity selector consists of a parallel plate capacitor placed in an outside magnetic field (see figure). Charged particles entering the velocity selector experience an electric and a magnetic force (neglect effects due to gravity). Given is the setup in the figure below (attached)
a) What is the direction of the magnetic force?
b) What is the direction of the electric force?
c) When the two forces are equal the particle will move straight through the velocity selector. Derive an expression for the speed v that fulfills this condition.
d) What happens to particles that have a speed larger than v? What happens to particles that have a speed smaller than v?
e) Protons move through a velocity selector with E = 2.0 · 10^5 N/C and B= 0.30 T. What is the speed of a proton that is not deflected?
[itex]\overline{}F[/itex]B=q[itex]\overline{}v[/itex] x [itex]\overline{}B[/itex]
[itex]\overline{}F[/itex]e = q[itex]\overline{}E[/itex]
FB=qVB
Fe=qE
a) up
b) down
c) qVB=qE
VB=E
V=B/E
d)it will deflect up, it will deflect down
e) v=(.30)/(2.0*10^5)= 1.5*10^-6 m/s
Just want to know if I am doing this correctly
A velocity selector consists of a parallel plate capacitor placed in an outside magnetic field (see figure). Charged particles entering the velocity selector experience an electric and a magnetic force (neglect effects due to gravity). Given is the setup in the figure below (attached)
a) What is the direction of the magnetic force?
b) What is the direction of the electric force?
c) When the two forces are equal the particle will move straight through the velocity selector. Derive an expression for the speed v that fulfills this condition.
d) What happens to particles that have a speed larger than v? What happens to particles that have a speed smaller than v?
e) Protons move through a velocity selector with E = 2.0 · 10^5 N/C and B= 0.30 T. What is the speed of a proton that is not deflected?
Homework Equations
(negatives are supposed to be vectors)[itex]\overline{}F[/itex]B=q[itex]\overline{}v[/itex] x [itex]\overline{}B[/itex]
[itex]\overline{}F[/itex]e = q[itex]\overline{}E[/itex]
FB=qVB
Fe=qE
The Attempt at a Solution
a) up
b) down
c) qVB=qE
VB=E
V=B/E
d)it will deflect up, it will deflect down
e) v=(.30)/(2.0*10^5)= 1.5*10^-6 m/s
Just want to know if I am doing this correctly