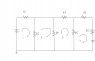
- #1
pat666
- 709
- 0
Homework Statement
Find the value of N(1,2,3) in attached circuit
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I've found i(1,2,3,4) from mesh analysis as:
[tex] i_1=1.44159mA,i_2=0.919142mA,i_3=0.396691mA,i_4=-0.08609047mA [/tex]
now I am having trouble finding N_2 and N_3 from this.
Thanks for any help.