- #1
vipulgoyal
- 26
- 0
Homework Statement
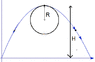
a stone is projected at an angle with the horizontal with velocity u. it executes a nearly circular motion near its maximum height for a short time. the radius of circular path is
??`
Homework Equations
answer is u2 sin2x/g3. The Attempt at a Solution
why isn't it is just the maximum height?
Last edited: