- #1
Dethrone
- 717
- 0
View attachment 4461
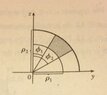
Part (a) is easy to do by setting up a triple integral, but for part (b), I was a bit confused by the diagram provided by the solutions manual:
View attachment 4462
Why is the spherical wedge (shaded) graphed on the z-y axis? In the most general case, shouldn't the two lines that form angle $\phi_1$ and $\phi_2$ be arbitrarily placed (such that $\phi < \pi /2$) and not necessarily lying on the z-y plane? Since it is to my understanding that $\phi$ is measured from the positive z-axis in any direction away from it, or did they draw it on the z-y plane for illustrative purposes?
Part (a) is easy to do by setting up a triple integral, but for part (b), I was a bit confused by the diagram provided by the solutions manual:
View attachment 4462
Why is the spherical wedge (shaded) graphed on the z-y axis? In the most general case, shouldn't the two lines that form angle $\phi_1$ and $\phi_2$ be arbitrarily placed (such that $\phi < \pi /2$) and not necessarily lying on the z-y plane? Since it is to my understanding that $\phi$ is measured from the positive z-axis in any direction away from it, or did they draw it on the z-y plane for illustrative purposes?
Attachments
Last edited: