- #1
Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- Working out constant of thermal conductivity and heat flow in a given time
- Relevant Equations
- Q/t = KA(T1 – T2)/L
Here is the Q below

I want to see if my values for part b) is okay?
This is what I have tried:

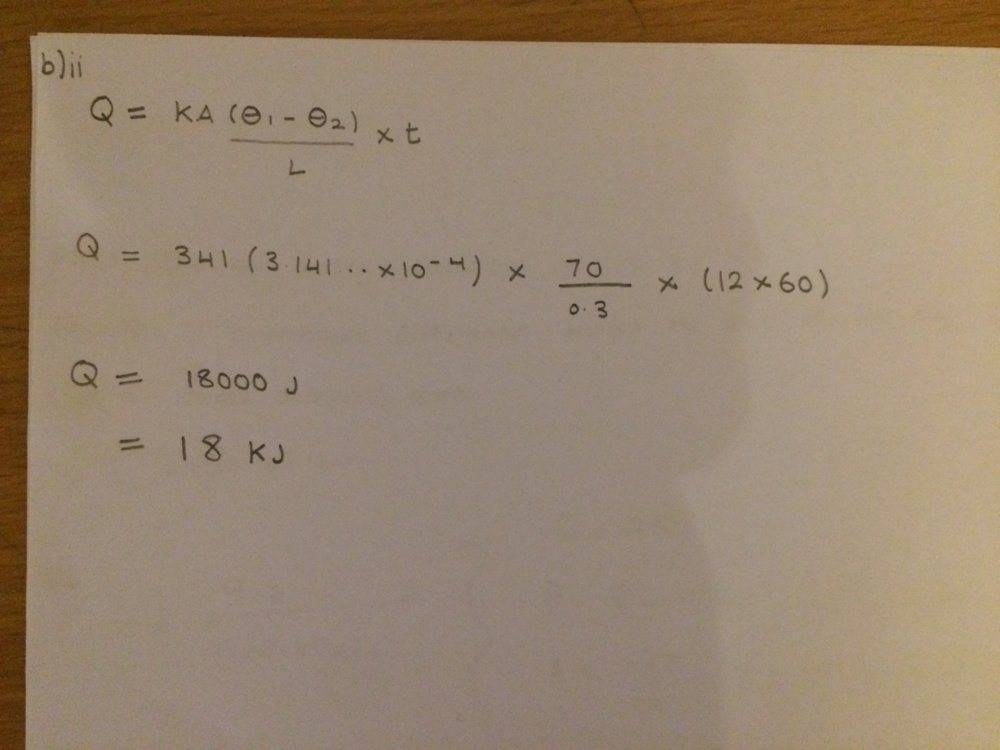
Any help would be nice! Thanks
I want to see if my values for part b) is okay?
This is what I have tried:
Any help would be nice! Thanks