- #1
maxelcat
- 33
- 4
This is a question from an a level textbook.
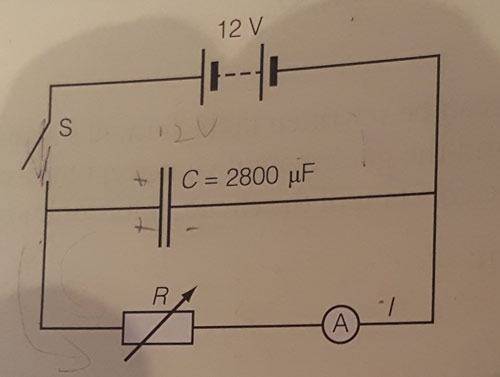
The R starts at 8k ohms (thought its not relevant)
Switch S is closed - C fully charges up.
Question:Switch S is opened. Explain why the current decreases and REVERSES direction in the ammeter.
This is what I think. The decrease in current is easy to explain but the REVERSE in direction is not.
But the questions says there is a reverse of I so something is wrong in my answer.
Can anyone please point out what I have got wrong!
Thanks
E
The R starts at 8k ohms (thought its not relevant)
Switch S is closed - C fully charges up.
Question:Switch S is opened. Explain why the current decreases and REVERSES direction in the ammeter.
This is what I think. The decrease in current is easy to explain but the REVERSE in direction is not.
- When the switch is closed current flows -> (anticlockwise) through the ammeter
- When the switch is opened current STILL flows anticlockwise as it leaves the capacitor.
But the questions says there is a reverse of I so something is wrong in my answer.
Can anyone please point out what I have got wrong!
Thanks
E