- #1
TheWire247
- 15
- 0
Homework Statement
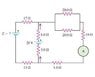
In the circuit shown in the link, the 6.0 \ohm resistor is consuming energy at a rate of 24.0 J/s when the current through it flows as shown.
A) Find the current through the ammeter A.
B) What is the polarity and emf of the battery \epsilon assuming it has negligible internal resistance?
session.masteringphysics.com/problemAsset/1267081/1/yg.19.62.jpg
Homework Equations
V=IR
V=ε-IR
The Attempt at a Solution
I am completely stuck so any help would be very much appreciated
Attachments
Last edited: