- #1
samaaa
- 48
- 0
Hi guys:I have a project to design ECG
i want to calculate the six leads(I,II,III,aVR,aVL and aVF) by this method:
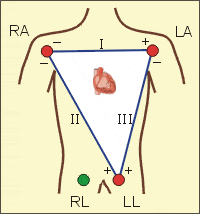
i will measure the voltage of three probe or electrode(RA,LA and LL) RL as a reference
by using DAC(digital to analog converter) the DAC connected to PC computer,
and then calculate(I,II,III,aVR,aVL and aVF) mathematically(by using matlab) according to these equations:
I=LA-RA,II=LL-RA,III=LL-LA,aVR=-((I+II)/2),aVL=I-(II/2) and aVF=II-(I/2)
so,what's your opinion about this method versus classical method(other methods)?
i want to calculate the six leads(I,II,III,aVR,aVL and aVF) by this method:
i will measure the voltage of three probe or electrode(RA,LA and LL) RL as a reference
by using DAC(digital to analog converter) the DAC connected to PC computer,
and then calculate(I,II,III,aVR,aVL and aVF) mathematically(by using matlab) according to these equations:
I=LA-RA,II=LL-RA,III=LL-LA,aVR=-((I+II)/2),aVL=I-(II/2) and aVF=II-(I/2)
so,what's your opinion about this method versus classical method(other methods)?