- #1
kuchun
- 11
- 1
I want to know the BJT implementation of flip flop with the help of proper circuit diagram..
I want to know the BJT implementation of RS flip flop...Thanks for ur replyPhrak said:There are RS (set-reset) flip flops, D flip flops, JK flip flops, and maybe a few others that have no useful function or advantage over those already given.
Which one did you have in mind?
As BJT technology has waned over the past couple two or three decades, given over to MOS technology, you may have trouble finding an online BJT equivalent circuit for a flip flop of any sort.
Thanx for your reply...it was really helpful for me...Can u suggest me some good books on digital electronics, I am at beginner level..vk6kro said:If you go to Google and set it to IMAGES, you can get lots of flip flop circuits.
The common one used as a divide-by-2 is the bistable flip flop.
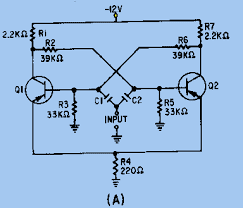
As you can see, it uses a lot of components and also requires careful adjustment of the bias resistors. After that, it is quite reliable. I know of one that was made in 1972 and is still operating.
These days you would certainly use an integrated circuit.
vk6kro said:The common one used as a divide-by-2 is the bistable flip flop.
A BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) flip flop circuit diagram is a logic circuit diagram that uses BJT transistors to store and manipulate binary data. It consists of two transistors connected in a feedback loop, with the output of one transistor connected to the input of the other.
A BJT flip flop circuit works by using the principles of feedback to store and manipulate binary data. When one transistor is turned on, it sends a signal to the other transistor to turn off, and vice versa. This allows the circuit to store and switch between two states, representing the two binary digits 0 and 1.
There are three main types of BJT flip flop circuits: the SR (Set-Reset) flip flop, the D (Data) flip flop, and the JK flip flop. The SR flip flop uses two inputs (S for set and R for reset) to control the output, the D flip flop uses a single data input to control the output, and the JK flip flop uses two inputs (J and K) to control the output and has the additional feature of being able to toggle between states.
Some advantages of using a BJT flip flop circuit include its simplicity, low cost, and reliability. It also has the ability to store and manipulate data without the need for external components, making it useful in a variety of digital applications such as memory, counters, and registers.
One limitation of using a BJT flip flop circuit is its slow speed compared to other types of flip flops such as CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) flip flops. It also requires a constant power source to maintain its stored data, making it unsuitable for low-power applications.