Lambda96
- 233
- 77
- Homework Statement
- show that the following applies ##\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \infty}^{\infty} g^{\epsilon}(x) \phi(x)dx = \phi(0)##
- Relevant Equations
- none
Hi,
I'm not sure if I have calculated task b correctly, and unfortunately I don't know what to do with task c?
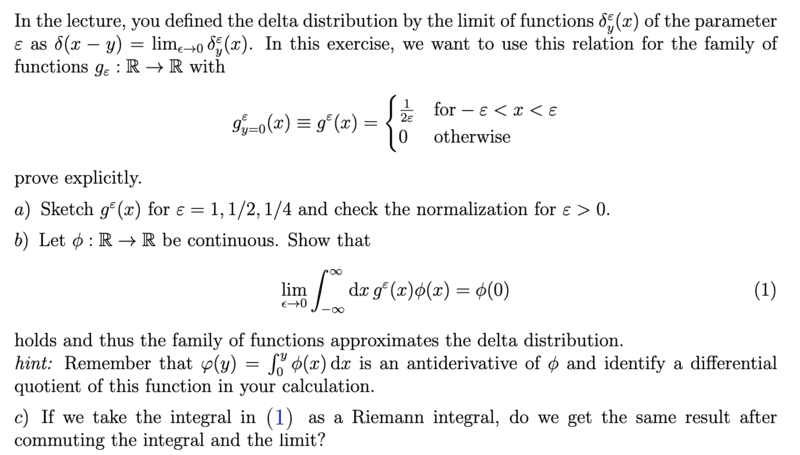
I solved task b as follows
##\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \infty}^{\infty} g^{\epsilon}(x) \phi(x)dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{\infty}^{\epsilon} 0 \phi(x)dx + \displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)dx +\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{\epsilon}^{\infty} 0 \phi(x)dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)dx = \displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \frac{\varphi(\epsilon) - \varphi(- \epsilon)}{2 \epsilon}= \phi(0)##
Does task c mean the following
##\int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x) dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \sum\limits_{x= -\epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)##
I'm not sure if I have calculated task b correctly, and unfortunately I don't know what to do with task c?
I solved task b as follows
##\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \infty}^{\infty} g^{\epsilon}(x) \phi(x)dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{\infty}^{\epsilon} 0 \phi(x)dx + \displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)dx +\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{\epsilon}^{\infty} 0 \phi(x)dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)dx = \displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \frac{\varphi(\epsilon) - \varphi(- \epsilon)}{2 \epsilon}= \phi(0)##
Does task c mean the following
##\int_{- \epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x) dx=\displaystyle{\lim_{\epsilon \to 0}} \sum\limits_{x= -\epsilon}^{\epsilon} \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \phi(x)##