- #1
Aladdin123
- 16
- 0
Hi
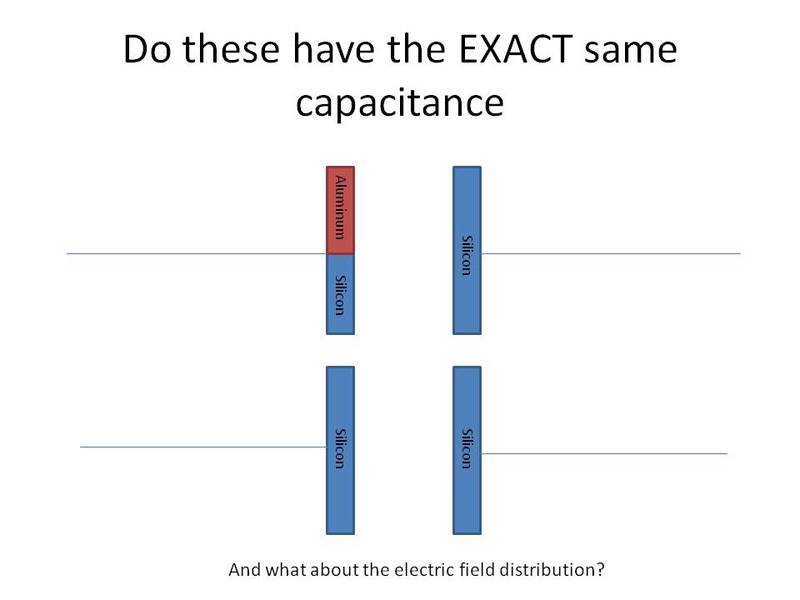
I was wondering about an issue i thought about while attending a masters thesis dissertation earlier
does the material of the plate (not the filling dielectric) affect capacitance (even if in the fringing level) ?
Check the attached picture , for a better explanation
I was wondering about an issue i thought about while attending a masters thesis dissertation earlier
does the material of the plate (not the filling dielectric) affect capacitance (even if in the fringing level) ?
Check the attached picture , for a better explanation
