- #1
Multiple_Authors
- 9
- 6
Multiple_Authors submitted a new PF Insights post
Does the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Imply Energy Nonconservation?
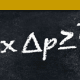
Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.
Does the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Imply Energy Nonconservation?
Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.