- #1
Spinnor
Gold Member
- 2,226
- 431
A high Q antenna basically means the antenna stores a large amount of energy in the near fields compared with the electromagnetic energy radiated per cycle?
When the alternating current momentarily stops in our half-wave antenna charge density is maximum at the ends of the antenna, and the electrostatic energy density is maximum near the poles of the antenna?
A quarter cycle latter the current density peaks and is maximum at the mid point of the antenna, and therefore magnetic energy density is momentarily maximum near the center of the antenna?
Is there then a cyclic flow of energy from the polar regions to the mid-section of our antenna and then back again (ignore the outward radial flow of energy which for a high Q antenna will be minor compared with near field energy density)?
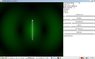
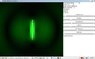
Are there any good Apps that show this cyclic flow of energy? I did find a great set of physics apps, one in particular that shows the energy density near the antenna but the results don't seem to fit my naive guess.
Screen shots below show the energy density near the antenna. The app is at,
http://www.falstad.com/emwave1/
which is from a large list of physics apps,
http://www.falstad.com/mathphysics.html
Thanks for any help!
Edit, the following crude picture of energy flow is more in line with my thoughts,
http://www.google.com/imgres?start=...0CCkQhBwwDDhk&iact=rc&dur=1778&page=6&ndsp=22
When the alternating current momentarily stops in our half-wave antenna charge density is maximum at the ends of the antenna, and the electrostatic energy density is maximum near the poles of the antenna?
A quarter cycle latter the current density peaks and is maximum at the mid point of the antenna, and therefore magnetic energy density is momentarily maximum near the center of the antenna?
Is there then a cyclic flow of energy from the polar regions to the mid-section of our antenna and then back again (ignore the outward radial flow of energy which for a high Q antenna will be minor compared with near field energy density)?
Are there any good Apps that show this cyclic flow of energy? I did find a great set of physics apps, one in particular that shows the energy density near the antenna but the results don't seem to fit my naive guess.
Screen shots below show the energy density near the antenna. The app is at,
http://www.falstad.com/emwave1/
which is from a large list of physics apps,
http://www.falstad.com/mathphysics.html
Thanks for any help!
Edit, the following crude picture of energy flow is more in line with my thoughts,
http://www.google.com/imgres?start=...0CCkQhBwwDDhk&iact=rc&dur=1778&page=6&ndsp=22
Attachments
Last edited: